Leadership and Communication | Exploring New Trends and Directions
- Other Laws|Blog|
- 15 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 6 July, 2024

Communication is the process by which information, ideas, thoughts, and emotions are exchanged between individuals or groups. It involves a sender transmitting a message through a medium to a receiver, who then interprets and understands the message. Effective communication is essential for coordination, collaboration, and achieving common goals within an organization or in everyday interactions. It can occur through various forms, including verbal, nonverbal, written, and digital means.
Table of Contents
Check out Taxmann's Business Organisation & Management | B.Com. | UGCF which gives fundamental clarity on the evolution of management, apprehends its effect on future managers, how organisations adapt to uncertain environments and decipher decision-making techniques. It is presented in simple, concise, crisp & lucid language for students of B.Com.
1. Communication
The word Communication is derived from Latin word ‘COMMUNIS’ which means COMMON in English. Communication is imperative to organizations as it helps the management to convey business plans and coordinate actions to attain objectives. It is a process in which one person expresses the ideas, emotions, thoughts to another. In other words, it assists interaction among people and enables one person to share the information to another. Effective communication is a precondition for executing managerial policies, as well as for controlling everyday activities, through human resources. Managerial staff focuses on communicating the information more effectively, so that goals can be easily attained. Managers who are good communicators, are likely to influence others towards common goals.
1.1 Definition
Let us now consider some definitions to understand what communication is:
- According to Cambridge Dictionary
“Communication means to share information with others by speaking, writing, moving your body, or using other signals”.
- According to Newstrom & Keith Davis
“Communication is the transfer of information form one person to It is a way of reaching others by transmitting ideas, feelings, thoughts, facts and values”.
- According to Theo Haiman
“Communication means the process of passing information and understanding from one person to another”.
- According to Koontz and Weihrich
“Communication is the transfer of information from a sender to a receiver, with the information being understood by the receiver”.
- According to Keith Davis
“Communication is a process of passing information and understanding from one person to another”.
1.2 Characteristics
From the above definitions, features of communication that can be drawn, which are as follows:
- Interaction among two or more persons: In communication process, it is essential that there should be presence of at least two persons as no individual can transfer ideas to oneself.
- Exchange of Thoughts: Communication takes place when some information is passed from one person to another. The process is said to be completed when one person exchanges his/her thoughts/ideas to another.
- Common Understanding: It is very crucial that the receiver should comprehend the message in the same sense in which it is being conveyed. Otherwise it would result in miscommunication.
- Objective of Communication: The main purpose of the transmitting information is to make receiver understand the message and respond accordingly.
- Dynamic Process: It is not a onetime rather evolving It keeps on changing according to the nature and purpose of message.
- Social Process: It is very important process for the survival of the human It is not possible to live in isolation or without interacting with others.
- Continuous Process: It is an ongoing In every field of business, communication is constantly required to maintain professional and personal relationships, so that business goals can be attained.
- Pervasive in nature: It is present in all types of Without communication, no organization can execute its policies. It is inevitable in nature.
- It can be direct or indirect: Communication can happen directly when sender and receiver are interacting face to It can also take place indirectly through other means, when sender and receiver are not present at a common place.
- Oral, written or symbolic: It is a process which can take place either in verbal, written or symbolic form.
1.3 Importance of effective Communication in an Organization
The following are the benefits of incorporating effective communication in the organization:
- Creates Relationships: Communication helps individuals to develop encouraging and constructive relationships with peers, through effective communication.
- Assists Innovation: It provides an environment to the employees to express their ideas, thoughts, and imaginations freely. It results in cultivation of innovative background, where employees can share their potential ideas.
- Constructs efficient Team: The organizations, that promote open communication result in creation of constructive teams. Open communication environment encourages employees to work towards common goals.
- Disseminates Information: It helps the managers to keep employees well informed about their roles and duties. This also facilitates managers to get feedback from employees, leading to productive relationships within the organization.
- Facilitates Decision Making: Communication helps in gathering information and data that facilitates decision making process. It provides necessary information to make decisions.
- Motivates Employees: Open communication environment builds confidence among employees and helps in removing misunderstandings and conflicts among employees.
- Action Oriented: It provides basis for taking action. It supplies information which is essential for making plans and taking actions.
- Contributes towards Organizational Success: Absence of proper communication in the organization hampers its growth and success.
1.4 Classification of Communication
In every organization, there are broadly two types of communication. The classification is done on the basis of channels of communication. The path through which information flows from one source to another is known as channel of communication. Communication can be of two types namely, Formal Communication and Informal Communication.
- Formal Communication: Formal communication implies official exchange of The course of communication is an intentional exercise. This results in easy flow of information to the end user without any obstruction. It involves flow of information through appropriate communication channel. The following are the types of formal communication:
- Verbal Communication: Verbal Communication is a type of oral communication wherein the message is transmitted through the spoken Here the sender gives words to his feelings, thoughts, ideas and opinions and expresses them in the form of speeches, discussions, presentations, and conversations.
- Nonverbal Communication: Nonverbal Communication (NVC) is the transmission of messages or signals through a nonverbal platform such as eye contact, facial expressions, gestures, posture, and body language.
- Informal Communication: Informal communication is casual communication between coworkers in the workplace. It is unofficial in nature and is based in the informal, social relationships that are formed in a workplace outside of the normal hierarchy of business structure. The informal communications are based on the personal or informal relations such as friends, peers, family, club members, etc. and thus is free from the organizational conventional rules and other In the business context, the informal communication is called as a “grapevine” as it is difficult to define the beginning and end of the communication.
1.4.1 Process
The process of communication is dynamic in nature as it starts with the conceptualization of ideas, thoughts by the sender who transfers the message to the recipient and the recipient provides the feedback to the sender within specified time period. The process is said to be completed when the receiver understands and interprets the message correctly. In the communication process, two or more persons are included and there are some steps that take place in order to ensure an effective and meaningful communication. Following steps are taken in order to complete the process of communication.
- Sender: The first and foremost step in communication process begins with the person, who wants to transfer some ideas, thoughts, information or emotion, to some other person. Sender is the communicator of the message. Sender generates and develops ideas and then encodes those ideas for transmission towards the recipient. The subject matter of communication, such as ideas, opinions, suggestions etc., needs to be converted into some tangible form. For that purpose, encoding is done by converting ideas into verbal or non-verbal forms like pictures, words, sentences etc.
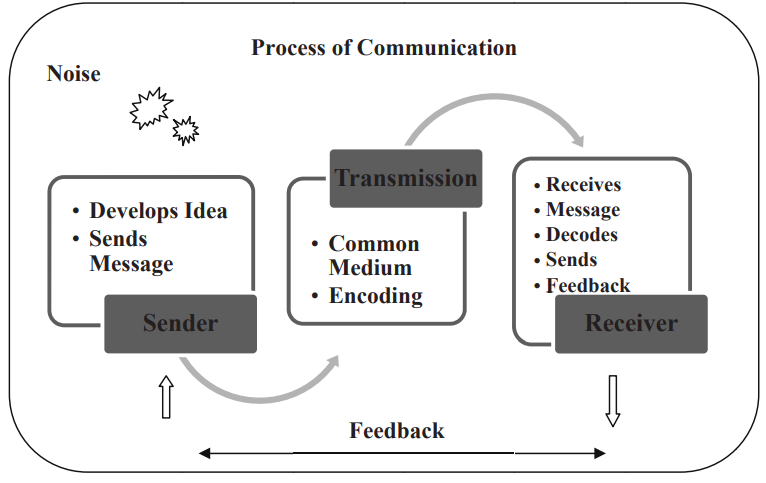
- Transmission of Message: The second step involves transfer of message from communicator to the recipient, known as the Receiver. Message can be transmitted by various formal or informal channels, such as telephone, telegraph, email, SMS, video calling etc. It passes on the information from sender to receiver and thus acts as a connector between both the parties.
- Receiver: In the next step, message reaches to the recipient who is generally the receiver of the message and to whom information is intended to be passed on. Once the message is received, he/she makes efforts to decode the information. During decoding process, receiver tries to translate the symbols decrypted by the communicator and interprets the meaningfulness of the message. The receiver should understand the message in the same spirit, that is intended by the sender. After understanding of the message, receiver can accept or reject the message and can use the information for further actions.
- Feedback: It is the last step, but it is the essence of communication process. It is given by the recipient to the communicator, conveying that the message is properly decoded, understood and interpreted. It provides an insight to the sender about the effectiveness of the communication process. Communication is a two way process but sometimes there are some disturbances during the process in the form of Noise.
Noise during Communication Process
According to Rosie Bunnow,
“The goal of all communication is understanding. Any- thing that interferes with this understanding is called noise”.
Noise is associated with some disturbance that occurs during the process of communication, that results in wrong influence on communication. Noise is a kind of hindrance, which disrupts the meaning of the message. It can happen at any point of time, during the commu- nication process. Noise can take place either at sender or receiver or both ends. Some examples of noise during communication process can be:
- A poor mobile network
- Wandering of thoughts
- Loud music playing
- Ambiguous encoding
- Speaker talking too fast
- An unread email
1.4.2 Barriers
There are various impediments to communication, which can occur at any point during communication process. The barriers could be due to semantics, organizational or personal reasons. Some of the most experienced barriers are being explained, briefly below:
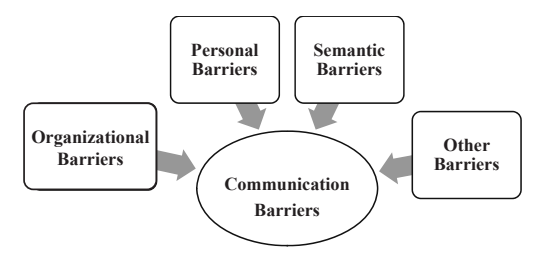
(i) Organizational Barriers: There are some barriers, which take place within the company. These occur in the form of the following:
| Complex Organizational Policies: There are some policies, which are very difficult to understand and interpret. These may result in delay in completion of work. | Complex and Complicated levels of Management: The organizations having complex hierarchy, result in delayed communication and message distortion. |
| Inadequate Facilities: For transmitting the message, different facilities required are internet, telephone connectivity, paper, and pen. Non accessibility results in delay of message transmission. | Poor Communication Policy: Organizations lacking in free communication policy, face bad social culture where employees hesitate to communicate. |
(ii) Personal Barriers: There are some barriers that take place within an individual. These occur in the form of the following:
| Emotional Disturbance: Emotional imbalance, such as hostility, fear, anger can covey wrong meanings to the message. | Apprehension: Apprehension about knowing little, may also create barrier in communication. |
| Personality Differences: Each person has unique personality. Sometimes seniors have superiority complex, which prevents them from engaging in communication with them. | Low Confidence: Low level employees opinions and suggestions are ignored by the management as result employees feel low in confidence |
| Absence of Mind: Inattention during communication process creates hindrance in conveying the correct message. Sometimes people are lost somewhere or preoccupied, during conversation due to illness, stress, family issues etc. | |
(iii) Semantic Barriers: There are some barriers that take place due to complexity of language. These occur in the form of the following:
| Usage of ambiguous words: Ambiguous sentences and words give different meaning to the communication. It leads to ineffectiveness in the communication process. | Usage of different language: When sender sends the message in a language which is not understood by the receiver then it leads to create a barrier in the communication |
| Usage of Technical Phrases: It sometimes becomes difficult for the receiver to comprehend the message, if technical words and phrases are used. | Wrongly Articulated Message: This barrier occurs due to badly expressed message, like wrong words and repetitiveness |
(iv) Other Barriers
| Perceptual Barrier: Different perceptions of things by different people. | Inattention: Not paying desired attention also hampers communication. |
| Personal Weakness: Sometimes sheer distrust and fear may prevent effective communication. | Structural Bottle necks: Too many intermediaries serve as a barrier in Organization Structure |
| Narrow/Closed Mind: Receiver may be resistant to not accept message or accept partially due to rigidity of mind. | Premature Evaluation: It means jumping to conclusion, even before the other person has finished communication. |
| Semantic Problems: All languages have an in built semantic problem, as words used may have more than one meaning. | Phonetic Barrier: This barrier is related to how words may sound, different, when spoken fast or heard from a distance. |
| Resistance to Communicate: The receiver may not be willing to communicate. | Differential Assumptions: When Sender takes certain assumption & does not share with the receiver, result in confusion. |
| Insensitive Listening: Selective listening or multi-tasking while the sender is sending message, also becomes a barrier in communication. | Wrong Channel of Communication: Selection of wrong media, time pressure disturbance in line etc. |
1.4.3 Ways to minimize Communication Barriers
There are some techniques to overcome abovementioned communication barriers, however, these can be minimized only, but cannot be removed completely, by following measures:
- It is very essential to maintain clarity in thoughts. Systematic and clear thoughts help in conveying the message correctly.
- It is required to create conducive environment that builds conviction and assurance among the parties.
- There should be proper coordination between speech and gestures. Otherwise it sometimes misleads the recipient.
- Usage of lucid and clear language is always appreciable.
- Transmission of message should be in a language that is well understood by the recipient.
- Organizations should form policies which encourage all levels of employees to communicate and express their thoughts, ideas, and feelings.
- It always advisable to remain active and attentive during communication, which means that effective listening should be adopted.
- Overloading of information should be avoided, as it may become difficult for the receiver to filter the information.
- Communicate should be made in a noiseless environment.
- Organizations should follow the format of short communication chains, as it helps in maintaining clarity and there are no chances of distortion of information.
- Organizations should ensure availability and accessibility of all the facilities that are needed for transmission of message.
- It is important to control emotions, during communicating the message.
- Feedback must be ensured, as it plays an indispensable role in an effective communication.
- Sender should be clear or intent, content and context of communication.
- Safeguards should be built in communication system to prevent transfer of conflicting and confusing information.
- Channel should be straight forward and short to minimize distortion and delay.
- Message and common medium should matched with messages.
- Internal environment of trust, goodwill, understanding and transparency should be built.
- All operational units should be efficiently connected with communication channels.
- Encourage upward communication.
- Patient and effective listening should be adopted by the manager.
- Encourage participative process.
- Communication system should be flexible.
- Strong MIS should be introduced to make communication effective.
- Long and complex messages must be in writing to avoid distortions.
- Caution should be exercised while communicating with semi-literates/non-professionals/persons working at lower level.
2. New Trends and Directions in Communication (Role of IT and Social Media)
There has been a revolution in the world of communication world over and in India, particularly, after the Government emphasized on the importance of digital communication. Also after the Covid-19 pandemic, the need for digital communication grew and new possibilities were explored. Since then, every single minute, there is an effort, somewhere, in the world to find new and better ways to achieve more efficient communication. Trends in communication seem to be moving so fast that it can be hard to keep up pace with them. Times are changing and the way we communicate in business has rapidly developed too. From telephones to cellular phones, and now the Internet, we are now more connected than ever before. The digital revolution has significantly changed business communication dimensions. The latest tools in online communications, help the business to move towards a future, where businesses have all the resources needed to provide their teams exchange of ideas, information, and input even, without having physical offices. For this, teams are encouraged to communicate more, as communication processes has become more seamless. And, teams which communicate more, are more likely to collaborate well and finish their assignments in the required quality and time frames. Following are some new tools and techniques being used to enhance digital communication.
- Faceless, Paperless & Cashless Operations: By the year 2024, the idea is to go fully faceless, cashless and paperless. Many researchers have called it a death of paper in the near The paperless future promised decades ago, has made substantial progress over the past two years, mainly due to the pandemic. A host of “no-contact” protocols and technologies have suddenly become familiar. From Omni channel, contactless delivery and curbside pickup, to QSR codes, Apple Pay, and workflow software, the momentum has swung irrevocably away from paper.
- Smart Documents: Smart documents also known as intelligent documents. These are files programmed with functions, which help the user to carry out work tasks. For example, Microsoft Office programs such as Word and Excel can be programmed with smart document solutions such as formulas and templates to speed up work solutions.
- Complete Automation: Most Communication is being made Even the meetings and conferences are mostly on the video conferencing mode or dual mode. Many offices have gone ‘Paper Less’ in the recent times, by boasting of being completely automated.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is shaping customer Service in a big way, in the recent times. AI is the ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent The term is frequently applied to the project of developing systems endowed with the intellectual processes characteristic of humans, such as the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize, or learn from past experience.
- Omni Channel Communication: Omni channel is a multichannel approach to sales that seeks to provide customers with a seamless shopping experience, whether they are shopping online from a desktop or mobile device, by telephone, or in a brick-and-mortar store. It is an approach that brings about integration between distribution, promotion and communication channels on the back end.
- Augmented Reality: Augmented reality (AR) is the real-time use of information in the form of text, graphics, audio and other virtual enhancements integrated with real-world It is this “real world” element that differentiates AR from virtual reality. AR integrates and adds value to the user’s interaction with the real world, versus a simulation. Customers are given a real feel with Augmented Reality.
- Virtual Reality: VR is not used just for video games It is the use of computer technology to create a simulated environment. Its most immediately-recognizable component is the head-mounted display (HMD). Human beings are visual creatures, and display technology is often the single biggest difference between immersive Virtual Reality systems and traditional user interfaces. Major players in Virtual Reality include HTC Vive, Oculus Rift and PlayStation VR (PSVR).
- Immersive Virtual Reality: This is the technology, which provides almost real and/or believable experience in a synthetic or virtual way. The goal of Immersive VR is to completely immerse the user inside the computer generated world, giving the impression to the user that he/she has “stepped inside” the synthetic world. This can be achieved by using either the technologies of Head-Mounted Display (HMD) or multiple projections.
- Blended Communication Channels: Blended communication leverages both. Press releases should be used to announce major news. They represent a point in time when a deal is reached, a product is launched or an appointment is made. However, companies can abuse them to disclose information with little or no news value.
- Live streaming: Live streaming is when the streamed video is sent over the Internet in real time, without first being recorded and Today, TV broadcasts, video game streams, and social media video can all be live-streamed. This technology is being used in a big way also.
- Video Conferences: Video conferencing is a technology that allows users in different locations to hold real-time face-to-face meetings, often at little to no There are many ways to utilize video conferencing technology, such as company meetings, job training sessions, or addressing board members.
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Cloud storage is a cloud computing model, which stores data on the Internet through a cloud computing provider, who manages and operates data storage as a service. It is delivered on demand with just-in-time capacity and costs, and eliminates buying and managing one’s own data storage infrastructure.
- Mobile Solutions: Businesses all over the world are constantly introducing the latest innovations and trends in their work A mobile app development solution is a recent innovation, which can transform a business tremendously. Mobile solutions refer to the online services that are made available to users while they are on the go. This technology has not only traversed geographical boundaries but has also accessed various domains.
- Digi-Locker: People found it difficult to keep important documents safe and be able to present them Targeted at the idea of paperless governance, Digi Locker is a platform for issuance and verification of documents & certificates in a digital way, thus eliminating the use of physical documents.
- Work chat apps: Team chat apps enable team members to engage, both on a personal and professional level. This is particularly important for remote teams without any other means of However, it is also beneficial for office teams to have another medium for engaging with their teammates.
- Google Chat: Google Chat is a communication service developed by Google. Initially designed for teams and business environments, it has since been made available for general consumers. It provides direct message, group conversations, and spaces, which allow users to create and assign tasks and share files in a central place in addition to It can be accessed through its own website and app or through the Gmail website and app.

- Slack: Slack is a messaging app for business that connects people to the information that they By bringing people together to work as one unified team, Slack transforms the way that organizations communicate.
- Track Finances: It is an expense tracker app, which allows the user to monitor and categorize expenses across different banks and investment accounts and credit cards.
- Making Notes, Recording calls, Sharing files & Signing Documents: Computing, now allows the user to create notes, record calls, and share files with multiple users simultaneously and also sign documents without having to pay for the digital signatures.
(#) Revolution – A hashtag is a word or a group of words preceded by a pound (#) sign, which is used to categorize and find conversations around a particular topic or trend, which is a clickable link to a group of posts using the same hashtag. Using hashtags is essentially a way to group together conversations or content around a certain topic, making it easy for people to find content that interests them. Hashtags can be used on just about any social media platform, such as instagram and twitter. Information can be traced with the help of this technique, even after many years.
2.1 Barriers to Digital Communication
Digital communication is expected to make communication between people easier, faster and better, but despite its conveniences, significant barriers to effective digital communication exist, both internally between coworkers and externally with the outside people organization interacts with. Following are some of the commonly experienced barriers:
- Accessibility barriers: Digital communication is effective only when people of all abilities can access and understand information.
- Semantic barriers: Semantic barriers are about the different interpretations of words and symbols used to communicate. This ambiguity is especially strong in digital communications, where trending hashtags, fast-flying memes and emojis can convey complex and evolving ideas.
- Physical barriers: These barriers present different challenges for offline versus online communication. Physical barriers to digital communication include other environmental conditions like time, place and medium.
- Emotional barriers: Emotional or psychological barriers are perhaps the most common barriers to communication, digital or otherwise, because individual’s beliefs, attitudes and values have a strong influence on how they process information.
- Identity barriers: These barriers include gender, racial, ethnic, sexual orientation, class, age, disability, or other personal, social or cultural identities.
- Credibility barriers: Credibility barriers interfere with digital communications, when people are not able to trust the message, the messenger, or both.
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied



 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
