Avoid Refund Failures & TDS Errors | Complete Guide to ITR Compliance
- ITR Week 2025-26|Blog|Income Tax|
- 8 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 9 September, 2025

A tax refund is a repayment to taxpayers of any excess amount paid to the government in taxes. This overpayment can occur for various reasons, such as errors in tax withholding from wages, overestimating tax payments, or eligibility for refundable tax credits. After the taxpayer files their tax return and the government verifies the overpayment, the excess amount is refunded, typically via direct deposit to the taxpayer's bank account.
FAQ 1. Is pre-validating a bank account on the e-filing portal mandatory to claim a refund?
The Income-tax Department mandates that taxpayers pre-validate their bank accounts on the e-filing portal to enable direct crediting of tax refunds. This step ensures that the account is active and owned by the taxpayer, minimising errors and fraud.
To pre-validate a bank account, Go to Profile>> My Bank Account>> Add Bank Account>> Provide the correct required details and validate.
On successful submission, a request will be sent to the respective bank or NPCI for validation. Once validation is successful, a taxpayer can nominate the bank account for a refund.
FAQ 2. ITR forms require details of the Legal Entity Identifier (LEI). What is it, and who needs to report it?
The Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) is a 20-character alpha-numeric code that uniquely identifies parties in financial transactions worldwide. It has been implemented to improve the quality and accuracy of financial data reporting systems for better risk management.
As per the RBI Regulations, all single payment transactions of Rs. 50 crores and above undertaken by entities (non-individuals) should include remitter and beneficiary LEI information. This applies to transactions undertaken through the NEFT and RTGS payment systems.
In accordance with RBI regulations, the new ITR Forms incorporate a column for furnishing details of the LEI number. A taxpayer is required to furnish the LEI details if he is seeking a refund of Rs. 50 crores or more.
FAQ 3. Can I claim the credit of tax deducted in advance on income that is taxable in subsequent years?
Certain provisions of TDS (including TCS) require the deduction of tax at source at the time of payment or at the time of credit, whichever occurs earlier. Advance payments are also subject to TDS. The Schedule of TDS/TCS in the ITR forms provides columns to fill in the information on tax deducted in previous years, but credit for the same is to be claimed in the future year. One cannot claim credit of TDS pertaining to income that is taxable in the subsequent year. Thus, such TDS credit can be carried forward to the subsequent year and can be claimed in the year income is offered to tax.
FAQ 4. I filed an income tax return to claim a tax refund, but it failed because I mentioned an incorrect bank account number. How can I submit the correct bank account number?
To submit the correct bank account number for a tax refund re-issue, follow these steps:
-
- Log in to incometax.gov.in
- Go to ‘Services’ and select ‘Refund Re-issue’.
- Select ‘Create Refund Re-issue Request’.
- Choose the record for which you want to submit a refund re-issue request.
- Select the bank account where you want to receive the refund.
- Click ‘Proceed to Verification’.
FAQ 5. What should I do in case of a TDS mismatch?
Credit for TDS as claimed in return may match with the balance appearing in Form 26AS, but the Assessing Officer still raises demand for payment of the differential amount of TDS. The CBDT [1] has highlighted that such tax credit mismatches may happen due to the following mistakes:
-
- Invalid/incorrect TAN of deductor
- Furnishing the same TAN for more than one deductor
- Filing information in wrong TDS Schedules in the Return Form
- Furnishing wrong challan particulars regarding Advance tax, Self-assessment tax, etc.
- Tax deducted by one deductor was wrongly included in the amount of tax deducted by another deductor.
Consequently, the tax credit could not be allowed to the taxpayers while processing returns despite the tax credit being available in the Form 26AS statement. The CBDT, therefore, has directed the taxpayers to verify if the demand raised is due to tax credit mismatch on account of such incorrect particulars and submit rectification requests with correct particulars of TDS/tax claims for correction of these demands. The rectification requests have to be submitted to the jurisdictional Assessing Officer if such an officer processes the return or the taxpayer is informed by CPC, Bengaluru, that such rectification is to be carried out by the Jurisdictional Assessing Officer. In all other cases of processing by CPC, Bangalore, an online rectification request can be made in the following manner:
Step 1:–Log in to the e-filing portal.
Step 2–Click on Services > Rectification
Step 3–On the next page, click New Request.
Step 4– Select the Assessment Year from the drop-down. Click Continue.
Step 5– On the next screen, select the option of ‘Tax Credit Mismatch Correction’ from the following types of Income-tax rectification requests:
(a) Reprocess the return
(b) Tax credit mismatch correction
(c) Additional information for 234C interest
(d) Status Correction
(e) Exemption section correction
(f) Return data correction (Offline)
(g) Return data correction (Online)
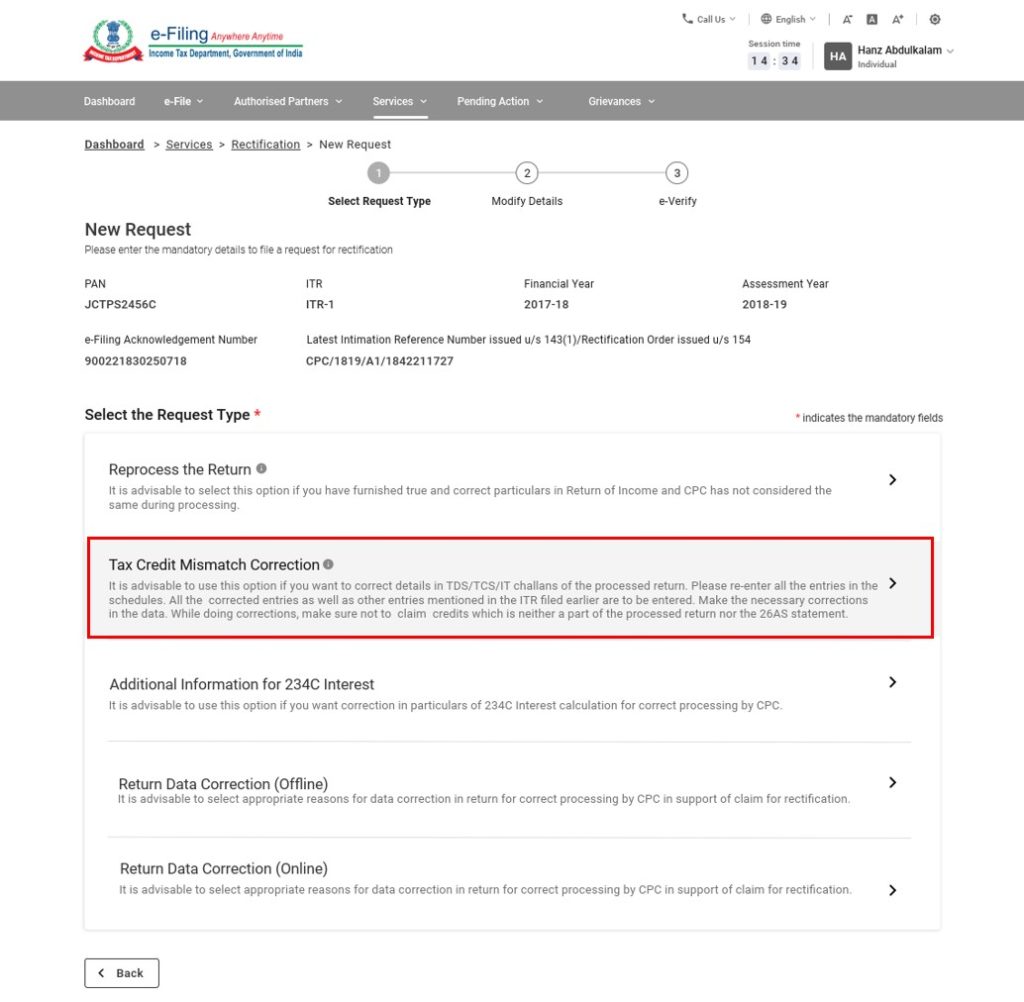
- Step 6 – The schedules under this request type are auto-populated based on the records available in the corresponding processed return. To edit or delete a schedule, select it and click Edit or Delete.
- Step 7 – Enter the correct details in the relevant schedules and click ‘Continue’ to submit the request.
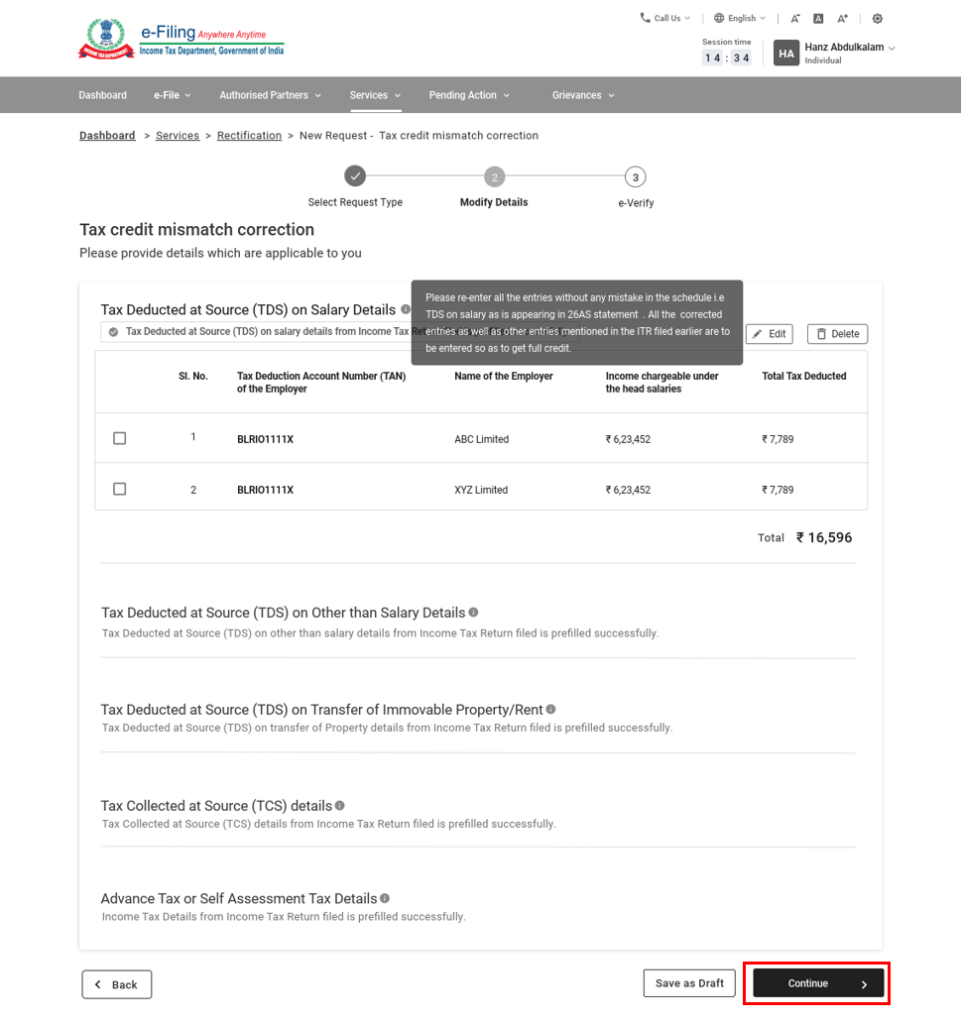
On submission, you will be taken to the verification page.
Where the TDS mismatch is due to an error in the TDS return filed by the deductor, you should approach the deductor to rectify the TDS return.
FAQ 6. How can you claim TDS credit in ITR if the deductor did not deposit TDS?
A taxpayer should approach his deductor and request to deposit TDS with the Government and file a TDS statement. However, he has no legal power to enforce the deductor to do so. Thus, if the deductor has refused the taxpayer’s request, he can submit TDS proof to the dept.
The ITR forms are annexure-less. Hence, a taxpayer cannot attach any supporting documents along with the ITR to support the TDS claim. Thus, it is advisable to file the ITR, claim TDS credit, and wait for its processing. Once the ITR is processed, the taxpayer will receive notice of a TDS mismatch.
Upon receiving such notice, he can file a reply and supporting documents showing that the TDS has been duly deducted from his income. The taxpayer can submit the salary slips to support his claim. Further, he can submit the bank statement showing credit for his net salary/other income after the deduction of TDS.
AO may allow the taxpayer a TDS credit if the documents submitted are found correct and cancel the demand raised by the CPC. However, if he does not allow the TDS credit, the taxpayer’s only option is to approach the Court.
It is essential to note Instruction No. 275/29/2014, dated 01-06-2015. The CBDT has directed that, as per Section 205, the assessee shall not be called upon to pay the tax to the extent tax has been deducted from his income where the tax is deductible at source under the provisions of Chapter XVII. Thus, the Act puts a bar on direct demand against the assessee in such cases, and the demand on account of tax credit mismatch cannot be enforced coercively. This may be brought to the notice of all the Assessing Officers that if the facts of the case so justify, the assessees are not put at any inconvenience on account of a default of deposit of tax into the Government account by the deductor.
| Read More Can I claim credit of TDS deducted by the employer but not paid by it to Govt.? on Taxmann.com/Practice |
FAQ 7. I have a bank fixed deposit of Rs. 1,50,000. My total income (including accrued interest on FDs) is below the taxable limit. How can I avoid the deduction of tax on interest income?
You can file a self-declaration to the bank in Form 15H if you are a senior citizen. Otherwise, you can file a self-declaration in Form 15G.
FAQ 8. How can I avoid a tax deduction if I earn an interest income of Rs. 40,000 from savings deposits, and my total income, including such interest income, is below the taxable limit?
If the interest payable on time deposits exceeds Rs. 40,000, the tax will be deducted under Section 194A. Interest payable on saving deposits does not attract TDS. To avoid the deduction of tax at source under Section 194A, the individual can furnish a declaration under Section 197A in Form 15G or Form 15H, as the case may be. Such a declaration can be furnished if the relevant income, in respect of which he is eligible to file a declaration, does not exceed the maximum exemption limit, and tax on his estimated total income for the financial year in which such income is to be included is nil.
FAQ 9. My return has been processed, and it shows an ‘Outstanding Tax Demand’. What should I do now?
You can respond to the outstanding demand online through the e-filing portal. Follow these steps:
- Log in to the e-filing portal.
- Navigate to Pending Actions > Response to Outstanding Demand to view a list of outstanding demands. To pay, click ‘Pay Now’.
- Click ‘Submit Response’ on the Response to Outstanding Amount page and proceed according to the situation:
-
- If the demand is correct and unpaid, select the relevant option, and you will be directed to the e-Pay tax page for payment. Successful payments will show a success message and a Transaction ID.
- If the demand is correct but already paid, add the challan details including Type of Payment, Challan Amount, BSR Code, Serial Number, and Date of Payment. Upload a copy of the challan and click Save. A success message and Transaction ID will be displayed upon validation.
- If you disagree with the demand (fully or partially), provide reasons for disagreement and confirm your submission. You will receive a success message and a Transaction ID.
Keep a record of the Transaction ID for future reference.
FAQ 10. The income-tax department has raised a demand against Mr A for the assessment year 2023-24. He did not pay the tax demand and filed an ITR for the next assessment year, claiming a refund. Can this refund be adjusted against his pending tax demand?
Yes, the CBDT has authorized the CPC to adjust tax demands against any refunds due to the assessee. Therefore, the refund claimed by Mr A for the next assessment year can be offset against the outstanding demand for the assessment year 2023-24.
FAQ 11. Should I pay a fee under Section 234F if there is a delay in filing my income tax return?
A fee under Section 234F is levied if the assessee does not furnish the return of income on the due dates prescribed under Section 139(1). The amount of such late filing fees shall be Rs. 5,000 if the return is furnished after the due date specified under section 139(1). However, if the total income of the person does not exceed Rs. 5 lakhs, then Rs. 1,000 shall be the late filing fees.
The late filing fee under Section 234F shall not apply to taxpayers where return filing is not mandatory, and the taxpayer is filing such return of income voluntarily.
| Read More Fee for default in furnishing return of income on Taxmann.com/Practice |
FAQ 12. I am a non-resident filing an Income-tax return in India. I do not maintain a bank account in India. Can I receive my tax refund in a foreign bank account?
Yes, the income-tax department allows non-residents to receive tax refunds in a foreign bank account. When filing the ITR, non-residents should provide the following details:
- SWIFT Code of the foreign bank account
- Name of the bank
- International Bank Account Number (IBAN)
[1] Press Note No. 402/92/2006, dated 17-04-2014,
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied





 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA

For AY 2021-22 (FY 2020-21) I filed my ITR on 14.09.2021 well within the time limit of the extended date intimated by ITD.
However, one of the Tax Deductors did not upload part of the TDS deducted by them before I filed my ITR on 14.09.2021 as a consequence of which I could not claim the TDS amount while filing my ITR as it was not reflecting in Form-26AS.
He uploaded the TDS deducted much later and it was reflecting in Form-26AS only in Dec, 2021. In the meantime my ITR for AY 2021-22 had been processed by the ITD.
How to claim this additional TDS deposited late by the Tax Deductor?
Hi, You can file an application under Section 154 from e-filing portal.
I have raised invoice for service in FY 2021-22 and showing as my income. But the customer has booked the same in FY 2022-23 and deducted TDS for AY2023-24. Do I need to pay tax not? Can I claim TDS credit in advance?
Hi Pankaj, There is no provision under the Income-tax Act that allow credit of TDS in advance. To claim the benefit of TDS, you need to ask the customer to revise his TDS return and show income in FY 2021-22. Once he revises the TDS return, you can file a revised ITR to claim the benefit of TDS.