PAN Card – What is PAN, Documents, Eligibility, and How to Apply for PAN Card
- Other Laws|Blog|
- 29 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 2 September, 2023
Table of Content-
- Introduction
- PAN Number Format
- Details Included in PAN Card
- Types of PAN Cards
- What are the benefits of a PAN Card?
- Documents Required for a PAN Card
- Who has to obtain PAN?
- When is it necessary to quote PAN?
- Interchangeability of PAN and Aadhaar
- Exemption from quoting PAN
- Consequences of Default
- How to apply for a PAN Card of an Individual?
- How to apply for a PAN Card of a Firm?
- How to Change the Citizenship Flag in PAN?
- How to submit a Grievance if Aadhaar cannot be linked with PAN?
- Why is PAN Card Important?
- Benefits of PAN Card
- FAQs

1. Introduction
The Permanent Account Number (PAN) is a ten-digit alphanumeric number issued for taxpayer identification in the form of a laminated card. PAN has to be mentioned in all communications with the Income-tax Dept. and in specified financial transactions which exceed the threshold limit. Aadhaar can also be used instead of PAN, effective September 1, 2019.
2. PAN Number Format
- Your full name.
- Your father’s name.
- A 10-digit code with letters and numbers that is your permanent account number (PAN).
- Your signature.
- Your date of birth.
- Your photograph.
- A hologram with the Government of India emblem and the Income Tax Department’s tag.
3. Details Included in PAN Card
PAN cards are used for identification and age proof, following Know Your Customer (KYC) rules. Here are the details found on a PAN card:
- Name of the individual or company who owns the card.
- Father’s name (for individual cardholders).
- Date of birth (for individuals) or date of registration (for companies).
- PAN Number – It’s a unique 10-character combination of letters andnumbers that carries specific information about the cardholder.
- The first three letters are always alphabetical (A to Z).
- The fourth letter indicates the taxpayer’s category.
Here are the different entities, along with their corresponding characters:
- A – Association of Persons
- B – Body of Individuals
- C – Company
- F – Firms
- G – Government
- H – Hindu Undivided Family
- L – Local Authority
- J – Artificial Judicial Person
- P – Individual
- T – Association of Persons for a Trust
The fifth letter in the PAN represents the initial letter of the individual’s surname.
The other letters and characters after that are random. The first four characters are numbers, and the last is a letter.
The PAN card also includes the individual’s signature, which is needed for financial transactions.
It has the person’s photograph as visual identification proof. However, corporations and firms have no photograph on the card.
4. Types of PAN Cards
Since PAN Cards are available for individuals and entities, you need to use different variants of Form 49 issued by the Government to apply for different types of PAN Cards. Here are the various types of PAN Cards and the corresponding Forms used to apply for them.
4.1 PAN Card for Individuals
The most common type of PAN Card is for individuals. To get this card, you must apply using Form 49A, available online on NSDL and UTIITSL websites. It’s not just for adults; even minors and students who are resident Indians can apply for this PAN card.
4.2 PAN Card for Non-Resident Individuals or Persons of Indian Origin
Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs) can get a PAN Card for tax purposes in India. They also need to fill out Form 49A to apply for this card.
4.3 PAN Card for Foreign Entities Paying Tax in India
Foreign firms or corporates registered outside India but paying taxes in India because of their business operations here can also get a PAN Card. To apply for this card, they must complete and submit Form 49AA as part of the application process.
4.4 PAN Card for OCI and NRE
In an exclusive twist, even Overseas Citizens of India and Non-Resident Entities can seek a PAN Card. To embark on this endeavour, they must engage with the distinguished Form 49AA, tailored precisely for their exceptional requirements.
4.5 PAN Card for Indian Companies
Companies and corporate entities registered and operational in India can apply for a PAN Card to facilitate financial and tax-related transactions.
Dive Deeper:
Employees Provident Fund – EPF Interest Rate, Withdrawal, Passbook.
Saving Schemes: Types, Interest Rates & Comparisons
5. What are the benefits of a PAN Card?
Apart from widely recognized identity proofs like the Aadhaar card and Voter ID, the PAN card is important in various procedures. It is mandatory for several essential tasks, including but not limited to:
- Filing Income Tax returns, where a PAN card is crucial.
- Avoid higher TDS deductions on interest income by providing your PAN to financial institutions.
- Linking your bank account to PAN for claiming tax refunds in case of excessive TDS deductions.
- Opening a new bank account requires a PAN card as mandatory identity proof.
- For transactions involving immovable assets (property and car) worth more than Rs. 10 lakhs.
- Financial transactions exceeding Rs. 50,000 necessitate submitting PAN details.
- When investing in mutual funds, bonds, or stocks, obtaining a PAN card is essential.
- A PAN card is indispensable for daily cash deposits exceeding Rs. 50,000.
- Payment of life insurance premiums exceeding Rs. 50,000 in a financial year.
These scenarios highlight the benefits of possessing a PAN card for taxpayers. However, its significance extends even further, benefiting the Income Tax authorities in several ways:
- Maintaining comprehensive records of individuals’ financial transactions and tax liabilities to strengthen the system.
- Facilitating more accurate tax rate determination based on individuals’ income.
- Assisting in precise calculations of total tax revenue earned by the country.
- Suppose individuals require a PAN card for activities where it is necessary. In that case, they can declare their unavailability in Form No. 60. However, it is essential to apply for a PAN card promptly and ensure eligibility before doing so.
6. Documents Required for a PAN Card
When applying for a PAN Card (using Form 49A or Form 49AA), certain essential documents need to be submitted for verification. The required documents vary depending on the applicant type. Below are the key documents needed for different entities applying for a PAN card:
A. Individual Applicant:
(i) Identity Proof (Copy of any one):
-
- Government-issued ID such as Aadhaar card, Driver’s License, Voter ID, etc.
- Arm’s License
- Pensioner Card with photograph
- Photo ID card from Central/State Government or Public Sector Undertaking
- Central Government Health Scheme Card or Ex-Servicemen’s Contributory Health Scheme Photo Card
- Original bank certificate on the bank’s letterhead, attested by the issuing officer, with an attested photograph and bank account number.
(ii) Address Proof (Copy of any one):
-
- Electricity, landline, or broadband connection bill
- Postpaid mobile phone bill
- Water bill
- LPG or piped gas connection bill or Gas Connection book
- Bank account statement
- Credit card statement
- Deposit account statement
- Post Office account Passbook
- Passport
- Voter’s ID Card
- Driving License
- Property registration document
- Domicile certificate issued by the Indian Government
- Aadhaar Card
- Original certificate from the employer (for reputed public or private corporations)
(iii) Proof of Date of Birth (Copy of any one):
-
- Birth certificate issued by Municipal Authority or authorized authority
- Matriculation certificate
- Pension Payment order
- Passport
- Marriage certificate issued by Registrar of Marriages
- Driving license
- Domicile certificate issued by the Indian Government
- Affidavit sworn before a magistrate stating the applicant’s date of birth
B. Hindu Undivided Family (HUF):
-
- Affidavit issued by the Karta of the HUF with details of coparceners (name, address, father’s name) on the application date.
- Identity proof, address proof, and date of birth proof for the Karta of the HUF (same as an individual).
C. Company registered in India:
-
- Copy of the Certificate of Registration issued by the Registrar of Companies.
D. Firms and Limited Liability Partnerships registered in India:
-
- Copy of the Certificate of Registration issued by the Registrar of Firms or Limited Liability Partnerships.
- Copy of the Partnership Deed.
E. Trust formed or registered in India:
-
- Copy of Trust Deed or Certificate of Registration Number issued by a Charity Commissioner.
F. Association of Persons:
-
- Copy of Agreement/Certificate of Registration Number from Registrar of Co-operative Society or Charity Commissioner or any document issued by the Central/State Government showing the identity and address of the applicant.
G. Individuals who are not Indian Citizens:
(i) Proof of Identity (Copy of any one):
-
- Passport
- Copy of PIO card issued by the Indian Government
- Copy of OCI Card issued by the Indian Government
- Copy of other national or citizenship Identification Number or TIN attested by applicable ‘Apostille’, Indian Embassy, High Commission, or Consulate where the applicant is based.
(ii) Address Proof (Copy of any one):
-
- Passport
- Copy of PIO card issued by the Indian Government
- Copy of OCI Card issued by the Indian Government
- Copy of other national or citizenship Identification Number or TIN attested by relevant ‘Apostille’, Indian Embassy, High Commission, or Consulate
- Copy of bank statement of the residential country
- Copy of NRE bank statement in India
- Copy of resident certificate or Residential permit
- Copy of registration certificate issued by FRO
- Copy of VISA granted and appointment letter from any Indian company.
7. Who has to obtain PAN?
The following persons should apply for Permanent Account Number (PAN). A resident person can apply for PAN in Form No. 49A , and a foreign citizen can apply in Form No. 49AA.
A person files SPICe+ to incorporate a company. By filing this form, the applicant can also apply for allotment of PAN. The company incorporation process has been changed from 23-02-2020, wherein PAN shall be allotted through Part B of the SPICe+ form, an integrated Web Form.
Further, a person who files Form FiLLiP to incorporate a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) can apply for allotment of PAN through the same form.
The following are the persons who are required to obtain PAN:
7.1 Persons having taxable income
Every person whose total income or the total income of any other person in respect of which he is assessable during any previous year exceeds the maximum exemption limit is required to apply for PAN. The application for allotment of PAN should be submitted before May 31 of the Assessment Year for which the income exceeds the maximum exemption limit.
7.2 Persons carrying on business or profession
Every person carrying on any business or profession shall apply for PAN if his total sales, turnover, or gross receipts exceed or are likely to exceed Rs. 5 lakhs during the financial year. In this case, it will be mandatory to apply for PAN, even if the assessee’s taxable income carrying on the business or profession is below the maximum exemption limit.
The application for allotment of PAN should be submitted before the end of the financial year for which gross receipt/turnover exceeds Rs. 5 lakhs.
7.3 Charitable Trust
Every person who receives income from property held under trust or other legal obligation, wholly or in part for charitable or religious purposes, and who is liable to be assessed as representative assessee regarding such income, must apply for PAN. Such a person shall apply for allotment of PAN before the end of the financial year.
7.4 Financial transaction of Rs. 2.5 lakhs or more
Any resident person (not being an individual) who enters into a financial transaction of an amount aggregating to Rs. 2.5 lakhs or more in a financial year is required to obtain PAN.
Further, any person who is acting as managing director, director, partner, trustee, author, founder, Karta, chief executive officer, principal officer or office bearer, or any person who is competent to act on behalf of the person, who has entered into a financial transaction of Rs. 2.5 lakhs or more in a financial year shall obtain PAN.
The application for allotment of PAN should be submitted on or before May 31, immediately following the financial year the financial transaction is made.
7.5 Persons whose income is subject to TDS/TCS
Every person entitled to receive any sum subject to a tax deduction or tax collection in any financial year shall apply for allotment of PAN before the end of such financial year .
7.6 Cash deposit of Rs. 20 lakhs or more
Every person, who intends to deposit cash in one or more accounts with a banking company, cooperative bank, or post office, shall be required to obtain PAN if the aggregate amount of cash deposited in such accounts during a financial year is Rs. 20 lakhs or more.
In this case, the person shall be required to obtain PAN at least seven days before the date on which he intends to deposit cash over the specified limit, i.e., 20 lakh or more .
7.7 Cash withdrawal of Rs. 20 lakh or more
Every person intending to withdraw cash from one or more accounts with a banking company, cooperative bank, or post office shall be required to obtain PAN if the aggregate amount of cash withdrawal from such accounts during a financial year is Rs. 20 lakh or more.
In this case, the person shall be required to obtain PAN at least seven days before the date on which he intends to withdraw cash over the specified limit, i.e., 20 lakh or more .
7.8 Open a current account or cash credit account
Any person who intends to open a current account or cash credit account with a banking company, a cooperative bank, or a Post Office shall be required to obtain PAN at least seven days before the date he intends to open such account .
7.9 Persons notified by the Central Govt.
The Central Government has notified the following persons who are required to apply for allotment of PAN:
| Person | Time limit to apply for PAN |
| Exporters and importers who are required to obtain an import-export code | Before making any export or import |
| Assessee applying for registration under Central Excise | Before making any application for registration |
| Assessee applying for registration under the GST Act | Before making any application for registration |
As per the GST Act, PAN is mandatory for regular taxpayers and casual taxable persons to apply for registration under GST. However, PAN is not required for a non-resident taxable person to obtain GST registration.
7.10 Notified persons of which specific info to be collected
To collect certain information that may be useful for or relevant to the purposes of this Act, the Central Government may specify any class of, or classes of persons to apply to the Assessing Officer for allotment of PAN within such time as may be specified. Such a person is required to apply for allotment of PAN irrespective of the fact that he is not liable to pay any tax under this Act or his turnover does not exceed the specified limit.
7.11 A person entering into specified transactions
Every person who intends to enter into specified transactions shall obtain PAN. These specified transactions shall be notified by the Board .
7.12 Any other person
Any person not covered under the above categories may voluntarily apply to the Assessing Officer for allotment of PAN. In such a case, the Assessing Officer shall allot the PAN to such a person. Besides the above cases, the Assessing Officer may also suo moto allot a PAN to any other person by whom tax is payable.
7.13 Allotment of the same PAN to multiple people
In the case the same PAN is allotted to more than one person, such cases shall be resolved in the following manner :
| 1st PAN holder | 2nd PAN holder | Resolution |
| Not filing return | Filing return | The first PAN holder will be allotted a new PAN, and the second PAN holder will continue to retain the original PAN |
| Not filing return | Not filing return | The first allottee will retain the original PAN, and the second allottee will be given a new PAN |
| Filed ITR for part years | Filed ITR for part years | The issue will be resolved after gathering information regarding the pending demands and refunds for those returns filed, with the approval of ADG(System)-I |
| Any other case | A resolution will be made after gathering information regarding the pending demands and refunds for the returns filed by the PAN holders, with the approval of ADG (System)-I. | |
8. When is it necessary to quote PAN?
8.1 If receipts are subject to TDS
Every person receiving any sum or income from which tax has to be deducted at source has to intimate their PAN to the person responsible for deducting such tax. If the payee fails to intimate his PAN to the payer, the tax shall be deducted at a higher rate in accordance with Section 206AA.
8.2 If payments are subject to TCS
Every buyer, licensee, or lessee paying any sum from which tax has been collected at source under Section 206C shall intimate his PAN to the seller responsible for collecting tax. If the collectee fails to furnish his PAN to the collector, then tax shall be collected at the highest rate in accordance with Section 206CC.
8.3 In all returns, challan, or correspondence
PAN must be quoted in all returns, correspondence with any Income-tax authority, and in challans for payment of any sum due under this Act. Further, the person responsible for the deduction and collection of tax at source shall mention his PAN in all TDS certificates and TCS Certificates issued to the person on whose behalf the tax has been deducted or collected, as the case may be.
8.4 In certain financial transactions
Every person (other than Central Govt., State Govt., and Consular Office) shall quote his PAN in all documents pertaining to the following transactions as specified in Rule 114B. These transactions shall be reported by the authorities or person concerned in Form No. 61A. To know more, refer to Statement of Financial Transaction or Reportable Account (SFT).
| Sr. No. | Nature of transaction | When is PAN required? |
| 1. | Sale or purchase of a motor vehicle (other than two-wheelers) | In all transactions |
| 2. | Opening an account [other than a basic savings bank deposit account] with a bank or a co-op. bank | In all transactions |
| 3. | A time deposit with a bank. co-op. bank, post office, Nidhi Co., or NBFC | If the amount of deposit exceeds Rs. 50,000 in each transaction or Rs. 5 lakhs in aggregate during a financial year |
| 4. | Deposit with a bank, co-op. bank or post office | If cash deposits exceed Rs. 50,000 during any one day |
| 5. | Purchase of bank drafts or pay orders or banker’s cheques from a bank or co-op. bank | If payment in cash exceeds Rs. 50,000 during any one day |
| 6. | Payment for one or more pre-paid payment instruments to a bank or co-op. bank or any other company or institution | If payment in cash or by way of a bank draft/pay order/banker’s cheque exceeds Rs. 50,000 in aggregate in a financial year |
| 7. | Making an application for the issuance of a credit or debit card | In all transactions |
| 8. | Opening of a Demat account | In all transactions |
| 9. | Payment to a Mutual Fund for the purchase of units | If the amount exceeds Rs. 50,000 |
| 10. | Payment to a company or an institution for acquiring debentures or bonds issued by it | If the amount exceeds Rs. 50,000 |
| 11. | Payment to the RBI for acquiring bonds issued by it | If the amount exceeds Rs. 50,000 |
| 12. | A contract for the sale or purchase of securities (other than shares) | If the amount exceeds Rs. 1 lakh per transaction |
| 13. | Sale or purchase of the shares of a company not listed in a recognized stock exchange. | If the amount exceeds Rs. 1 lakh per transaction |
| 14. | The Payment as a life insurance premium to an insurer | If the total amount exceeds Rs. 50,000 in a financial year |
| 15. | Payment to a hotel or restaurant against a bill or bills at any one time. | If payment in cash exceeds Rs. 50,000 |
| 16. | Payment in connection with travel to any foreign country | If payment in cash exceeds Rs. 50,000 |
| 17. | Payment for the purchase of any foreign currency at any one time | If payment in cash exceeds Rs. 50,000 |
| 18. | Sale or purchase of any immovable property | If the amount exceeds Rs. 10 lakhs or value as per stamp valuation authority exceeds Rs. 10 lakhs. |
| 19. | Any other transaction of sale or purchase, by any person, of goods or services | If the amount exceeds Rs. 2 lakhs per transaction |
8.5 Intimation of PAN
Any person, who receives documents regarding the financial transactions as referred to in the above table, shall ensure that PAN has been correctly furnished and has been mentioned in such document. If PAN is not available, he shall ensure that a declaration in Form 60 has been duly provided with complete particulars.
Such persons shall electronically furnish a statement in Form No. 61 through the reporting portal https://report.insight.gov.in/ containing particulars of the declaration received in Form 60. Such a person is also required to retain Form No. 60 for a period of 6 years from the end of the financial year in which the transaction is undertaken.
Form No. 61 shall be filled half-yearly as follows:
| Period | Due date |
| Declarations in Form No. 60 received during the 1st half-year (between April 1 to September 30) | On or before October 31 |
| Declarations in Form No. 60 received during 2nd half-year (between October 1 and March 31) | On or before April 30 |
9. Interchangeability of PAN and Aadhaar
9.1 Enabling Provision
Section 139A(5E) allows the interchangeability of Aadhaar with PAN. Thus, where a person has not been allotted PAN but possesses the Aadhaar, he may furnish his Aadhaar number in place of PAN, and such person shall be allotted a PAN in the prescribed manner.
Further, every person who has been allotted a PAN and who has linked his Aadhaar number with PAN as per section 139AA may furnish his Aadhaar number in place of a PAN for all the transactions where quoting of PAN is mandatory as per Income-tax Act.
9.2 Allotment of PAN based on Aadhaar
Where a person does not have a PAN but possesses an Aadhaar and furnishes, intimates, or quotes his Aadhaar in the specified transactions where PAN is mandatory, he shall be deemed to have applied for the PAN. He shall not be required again to apply or submit any documents for allotment of PAN.
Any person, who has not been allotted a PAN but possesses an Aadhaar, may apply for allotment of PAN by intimating his Aadhaar number. He shall not be required to apply or submit any documents for allotment of PAN. The Government has enabled functionality on the e-filing portal, i.e., https://www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in/home, to obtain a PAN based on the applicant’s Aadhaar instantly.
9.3 Quoting of PAN or Aadhaar in respect of specified transactions
Every person (except Central Government, the State Government, or the Consular Office) who enters into the following transactions shall quote his PAN or Aadhaar in all the documents pertaining to such transactions. He shall also authenticate his PAN or Aadhaar. Further, the recipient of such documents shall also ensure that the PAN or Aadhaar has been duly quoted and authenticated.
9.3-1. A cash deposit of Rs. 20 lakh or more
Every person, who intends to deposit cash in one or more accounts with a banking company, cooperative bank, or post office, shall be required to quote and authenticate his PAN or Aadhaar in all the documents about such transactions if the aggregate amount of cash deposit in such accounts during a financial year is Rs. 20 lakh or more .
9.3-2. Cash withdrawal of Rs. 20 lakh or more
Every person, who intends to withdraw cash from one or more accounts with a banking company, cooperative bank, or post office, shall be required to quote and authenticate his PAN or Aadhaar in all the documents about such transactions if the aggregate amount of cash withdrawal from such accounts during a financial year is Rs. 20 lakh or more .
9.3-3. Open a current account or cash credit account
Any person who intends to open a current account or cash credit account with a banking company, a cooperative bank, or a Post Office shall be required to quote and authenticate his PAN or Aadhaar in all the documents about such transactions .
9.4. Authentication of PAN or Aadhaar
Authentication is a process by which an individual’s PAN or Aadhaar number is submitted along with demographic or biometric information to the Income-tax Authority or other authority or agency for verification. Such authority or agency verifies the correctness or the lack thereof based on the information available with it.
Dive Deeper:
Aadhar Card (आधार कार्ड) – Get Aadhaar Card Complete Information Online
10. Exemption from quoting PAN
There may be certain situations wherein a person is unable to quote his PAN in the specified transactions, as referred to in the above table. These situations shall be dealt with in accordance with the following.
10.1 In case of a minor
Where a minor person, entering into any transaction, does not have any income chargeable to income-tax, he shall quote the PAN of his father or mother or guardian, as the case may be, in the relevant document.
10.2 In case a person doesn’t have taxable income
Where a person does not have PAN, he can make a declaration in Form 60 giving therein the particulars of such transaction. The declaration in Form No. 60 can be made either in paper form or electronically under the Electronic Verification Code.
The CBDT has clarified that in case of a cash sale of agricultural produce by its cultivator to the trader for an amount of less than Rs. 2 lakh, the cultivator will not be required to quote his PAN or to furnish Form No. 60.
10.3 In the case of non-resident
If a non-resident person does not have a PAN, he shall not be required to mention the PAN in the following transactions:
(a) For making an application for issuance of a credit card or debit card;
(b) Cash payment to a hotel or restaurant, even if it exceeds Rs. 50,000;
(c) Cash payment in connection with travel to any foreign country, even if it exceeds Rs. 50,000;
(d) Cash payment for the purchase of any foreign currency, even if its value exceeds Rs. 50,000;
(e) Payment to the RBI for acquiring bonds issued by it;
(f) Payment to banks for purchase of bank drafts or pay orders or banker’s cheques;
(g) Payment to a bank, co-op. bank or any other company or institution for pre-paid payment instruments;
(h) Any other transaction of sale or purchase, even if the amount exceeds Rs. 2 lakhs per transaction.
In all other transactions, the non-resident person shall quote his PAN in all records relating to these transactions.
10.4 In case of investment by a non-resident in AIF
As per Rule 114AB, a non-resident, not being a company or a foreign company, shall not be required to obtain and quote PAN if the following conditions are satisfied[16] :
(a) Assessee has made an investment in Category-I or Category-II Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) located in the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) or a Category III AIF which fulfills the conditions of being a specified fund as referred under Section 10(4D);
(b) Assessee does not earn any income in India other than the income from investment in the aforesaid AIFs during the previous year;
(c) Income-tax due on such income has been deducted at source and remitted to the Central Government by such AIF at the rates specified in Section 194LBB; and
(d) Assessee has furnished the following details and documents to the AIF:
-
- Name, e-mail id, and contact number;
- Address in the country or specified territory of which he is a resident;
- A declaration that he is a resident of a country or specified territory outside India; and
- Tax Identification Number allotted in his home country, and if such number is not available, then a unique number based on which he is identified by the Government of his home country.
Further, such AIF is required to furnish a quarterly statement electronically in Form No. 49BA and upload a declaration received from the assessee within 15 days from the end of the quarter in which such details or documents are received by it.
A non-resident or foreign company satisfying the above conditions is exempted from filing a return of income as well, provided he has not been issued a notice for filing a return of income under provisions of Section 142(1) or Section 148 or Section 153A or Section 153C for the relevant assessment year.
10.5 In case of investment by a non-resident in specified securities
As per Rule 114AAB, a non-resident, being an Eligible Foreign Investor (EFI), shall not be required to obtain and quote PAN if the following conditions are satisfied:
(a) He operates in accordance with SEBI’s circular.
(b) He has made transactions only in the capital asset referred to in Section 47(viiab), which are listed on a recognized stock exchange located in any IFSC;
(c) The consideration on transfer of the capital mentioned above asset should be paid or payable in foreign currency;
(d) He does not earn any income in India other than the income from the transfer of capital mentioned above asset; and
(e) He has furnished the following details and documents to the stock broker through which the transaction is made:
-
- Name, e-mail id, and contact number;
- Address in the country or specified territory of which he is a resident;
- A declaration that he is a resident of a country or specified territory outside India; and
- Tax Identification Number allotted in his home country, and if such number is not available, then a unique number based on which he is identified by the Government of his home country.
Further, the stock broker shall be required to furnish a quarterly statement electronically in Form No. 49BA and upload a declaration received from EFI within 15 days from the end of the quarter in which such details or documents are received by it.
An eligible foreign investor satisfying the above conditions is exempted from filing a return of income as well, provided he has not been issued a notice for filing a return of income under provisions of Section 142(1) or Section 148 or Section 153A, or Section 153C for the relevant assessment year.
11. Consequences of default
11.1 In case of failure to obtain PAN
If a person is required to obtain a PAN but fails to obtain the same, he shall be liable for a penalty under Section 272B.
11.2 In case multiple PANs are obtained
A person who has been allotted a PAN is strictly prohibited from applying for another PAN. In case of any default, the applicant shall be liable to a penalty under Section 272B.
11.3 In case of failure to quote PAN or Aadhaar
If a person fails to quote or intimate his PAN or Aadhaar or quotes or intimates a false PAN or Aadhaar, which he either knows or believes to be false or does not believe to be true, he shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 10,000 for each such default.
11.4 In case of failure to authenticate PAN or Aadhaar
If a person fails to authenticate the PAN or Aadhaar in documents relating to the specified transaction, he shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 10,000 for each default.
11.5 Failure to ensure quoting of PAN or Aadhaar
Every person receiving any document relating to the specified transactions shall ensure that the PAN or Aadhaar has been quoted in the document and authenticated in the prescribed manner. In case of any failure, he shall be liable for payment of Rs. 10,000 as a penalty for each such default.
12. How to apply for a PAN Card ofan Individual?
The Permanent Account Number (PAN) is a ten-digit alphanumeric number issued for taxpayer identification. PAN has to be mentioned in all communications with the Income-tax Dept. and in specified financial transactions which exceed the threshold limit.
A resident person can apply for PAN in Form No. 49A, and a foreign citizen can apply in Form No. 49AA.
The Department has also launched an Aadhaar-based instant PAN allotment service. If a person applying for PAN has a valid Aadhaar number issued by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), he can opt for this service. Foreign Citizens cannot apply for PAN using this service.
This PAN is paperless, online, and free of cost. This facility is only for those applicants who have an Aadhaar number from UIDAI and have registered their mobile number with Aadhaar. Applicants applying under this service will only be issued an e-PAN, which is also a valid form of PAN.
The PAN Card be applied in the following ways:
- Instant E-PANthrough Income-tax E-filing Portal (https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal/)
- Normal PAN through Protean Portal (https://www.protean-tinpan.com/)
Steps to Apply for PAN through Protean Portal
This tutorial explains how an Individual can apply for PAN in Form 49A. Here is a step-by-step procedure to apply for PAN.
Step 1: Visit https://www.protean-tinpan.com/
Step 2: Go to Services>PAN

Step 3: Click on ‘Apply’
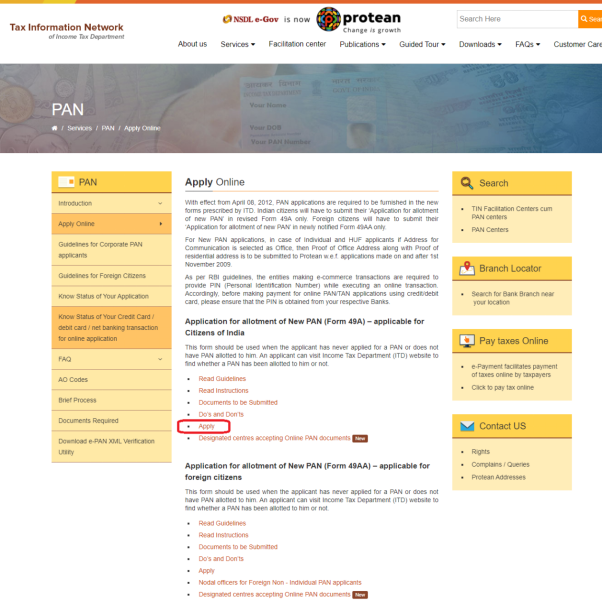
Step 4: Select the type of PAN application, category, and Applicant’s details and click ‘Submit’
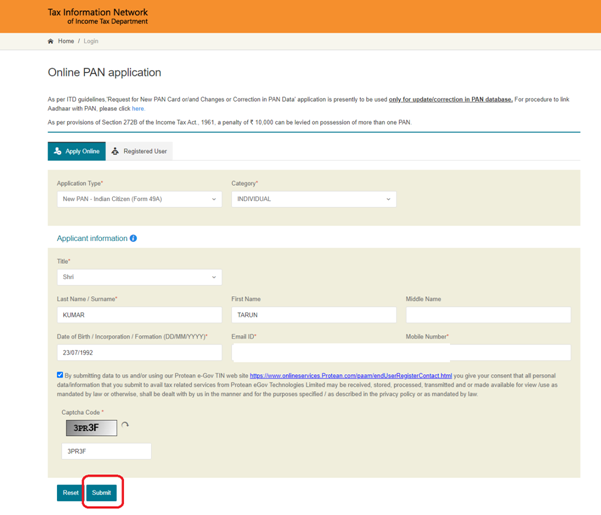
Step 5: On submission, a Token Number will be generated. Click on ‘Continue with PAN Application Form
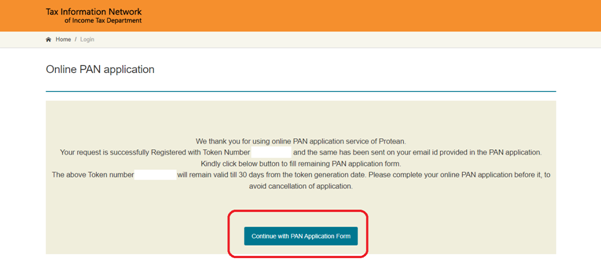
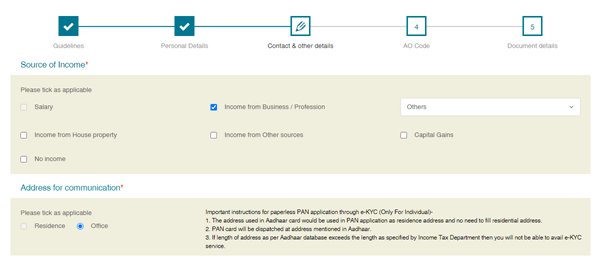
Step 6: Fill in the details asked in the PAN application form:
(a) Fill in ‘Personal Details’ and click on ‘Next’
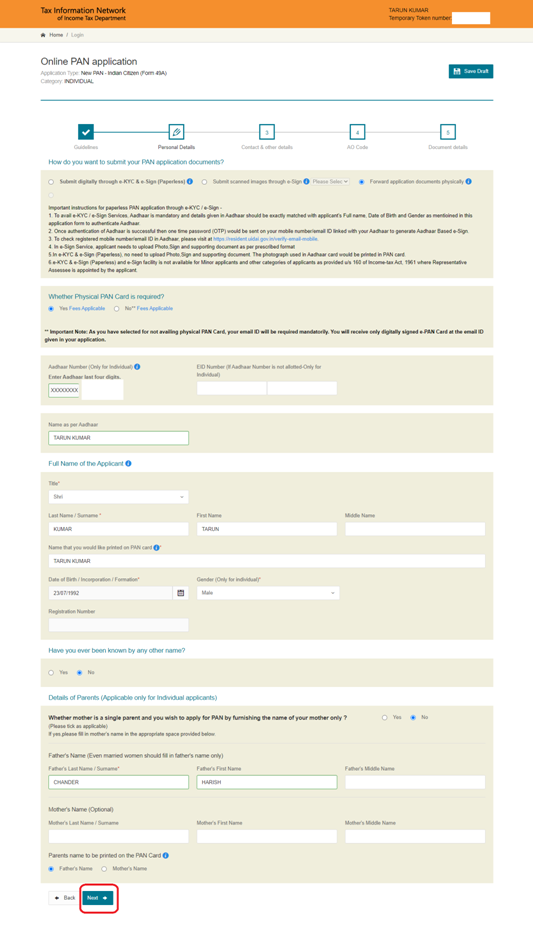
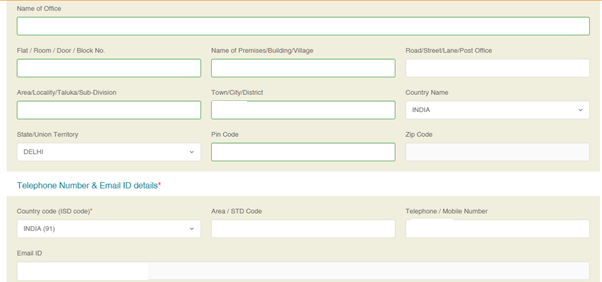
(b) Fill in the Contact details and click on ‘Next’
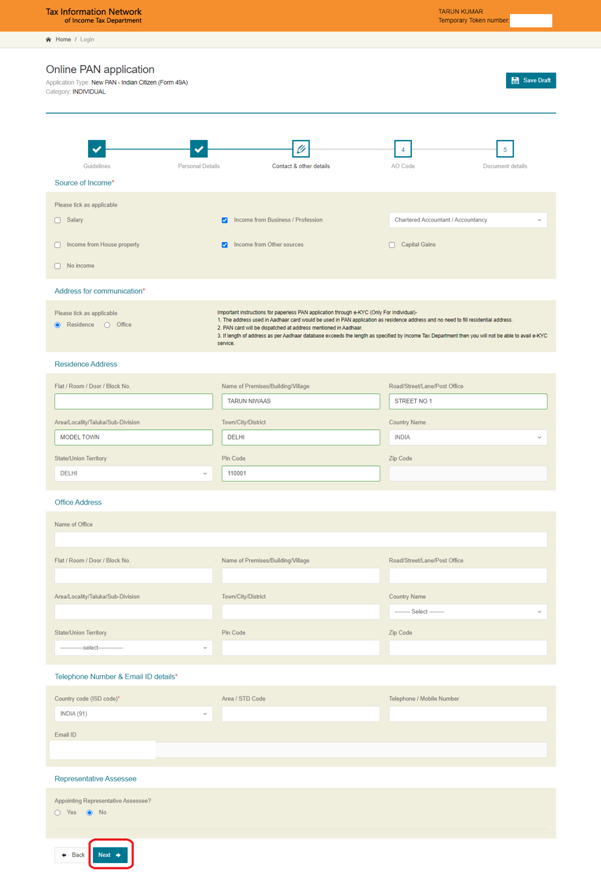
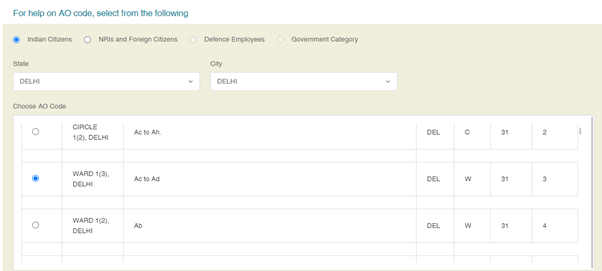
(c) Select AO Code and click on ‘Next’
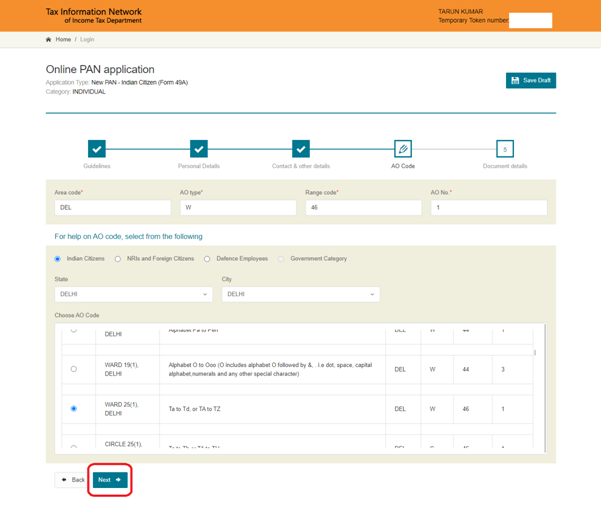
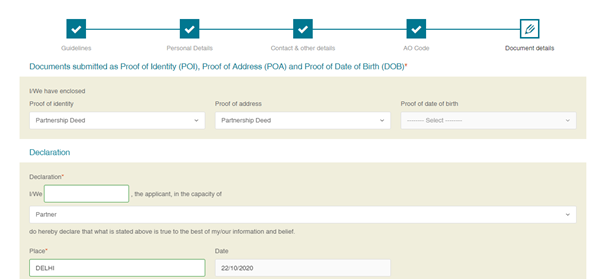
(d)Select the Documents submitted as Proof of Identity (POI), Proof of Address (POA), and Proof of Date of Birth (DOB) and Click ‘Submit’
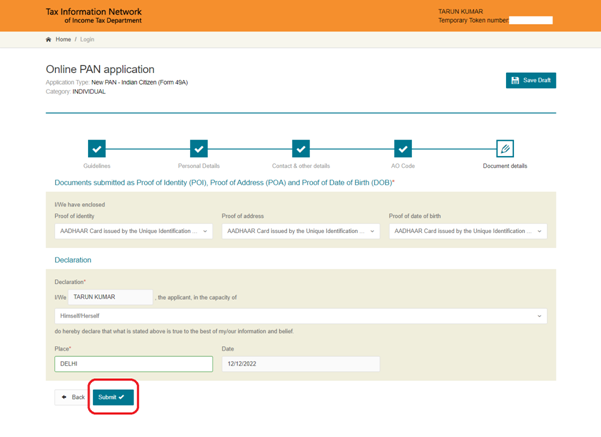
Step 7: Verify the details in the Form and Click ‘Proceed’.
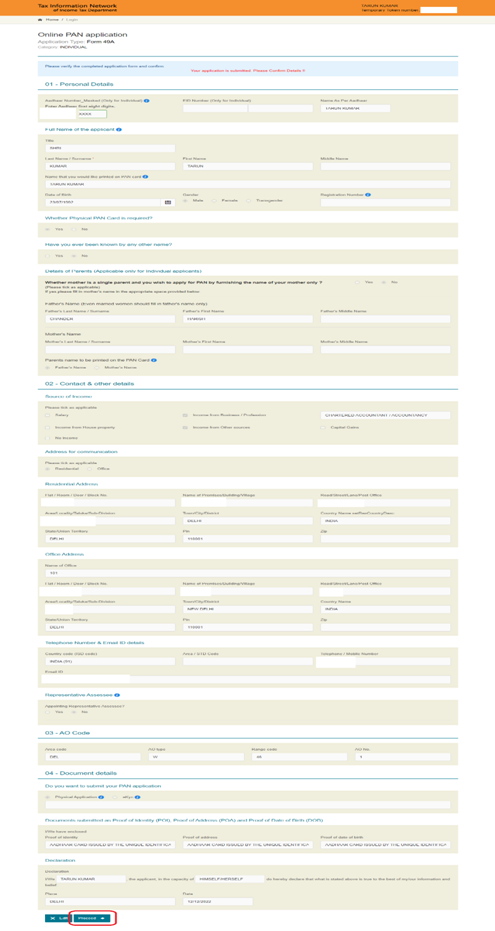
Step 8: Choose the preferred mode of payment.
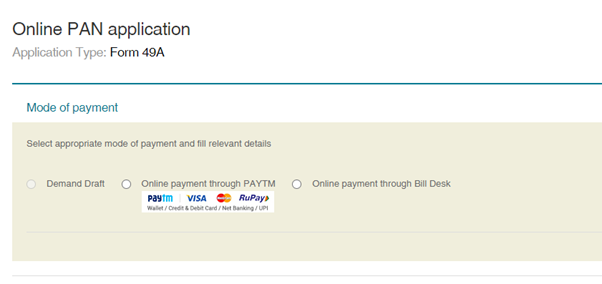
Step 9: Make the payment
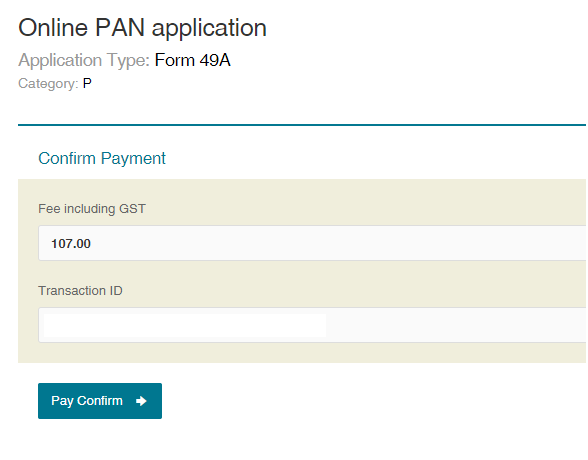
Step 10: You will be redirected to the bank site
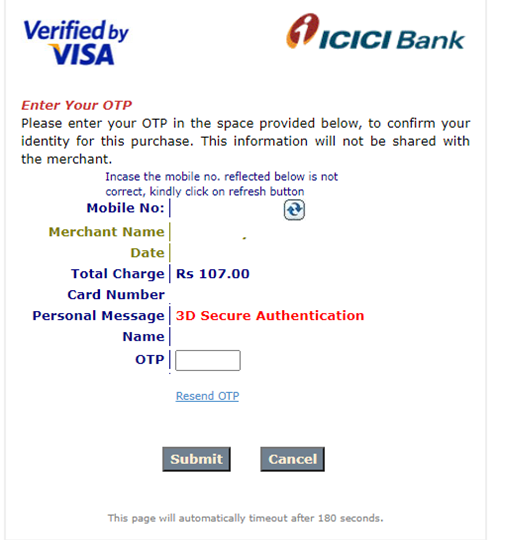
Step 11: Download the Payment Acknowledgment
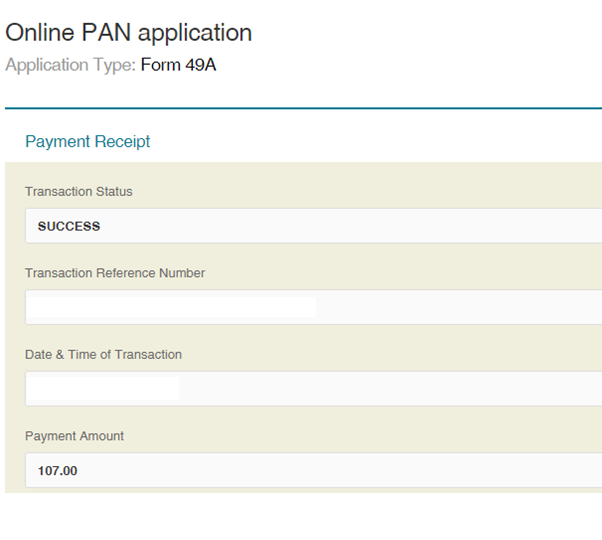
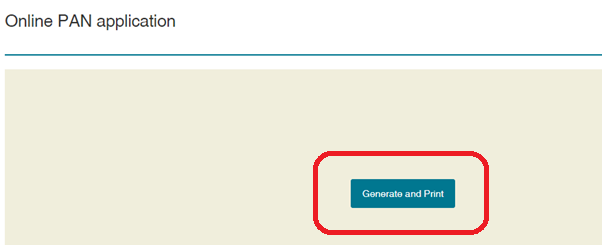
Step 12: Download and Print the PAN Application
Submit the signed application and documents to designated centres or post at:
INCOME TAX PAN SERVICES UNIT
Protean eGov Technologies Limited
4th Floor, Mantri Sterling, Plot No. 341,
Survey No. 997/8, Model Colony,
Near Deep Bungalow Chowk,
Pune – 411 016
PAN/TDS Call Centre: 020 – 27218080 | Fax: 020 – 27218081
e-mail: tininfo@nsdl.co.in
13. How to apply for a PAN Card of a Firm?
Steps to Apply PAN
This tutorial explains how the firm can apply for PAN in Form 49A. Here is a step-by-step procedure to apply for PAN.
Step 1: Visit
https://www.onlineservices.nsdl.com/paam/endUserRegisterContact.html
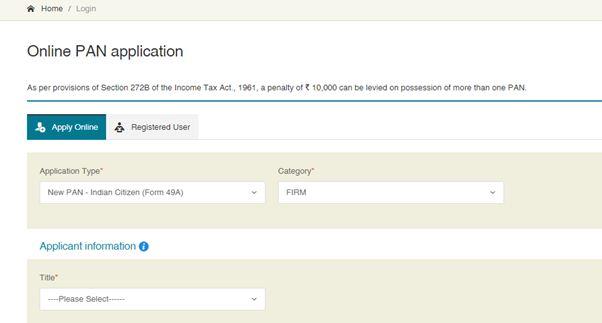
Step 2: Select the type of PAN application, category, and applicant’s details and click ‘Submit’
Step 3: On submission, a Token Number will be generated. Click on ‘Continue with PAN Application Form’
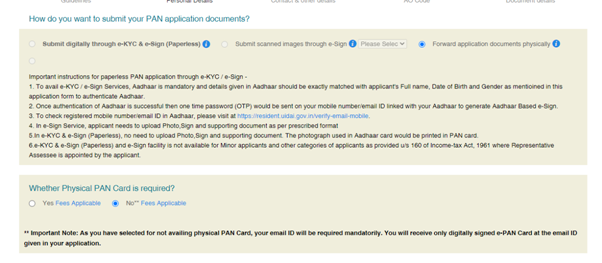
Step 4: Fill in the details asked in the PAN application form and Click ‘Submit’
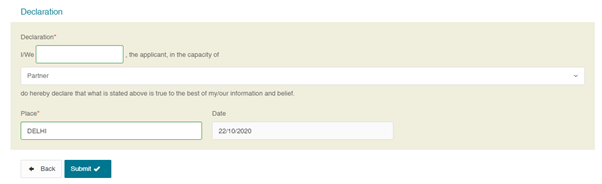
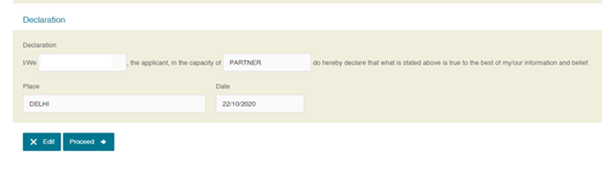
Step 5: Verify the details and Click ‘Proceed’.
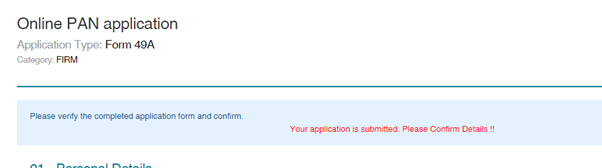
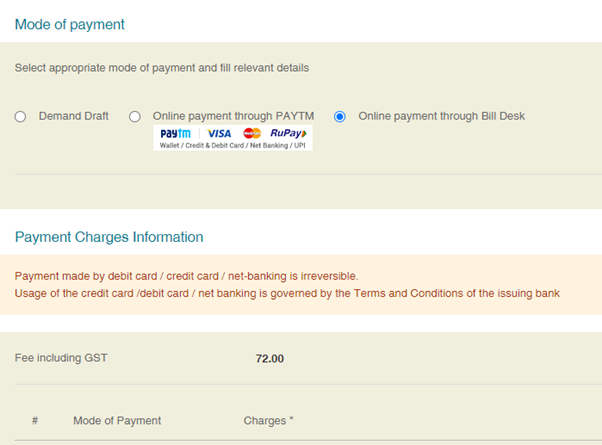
Step 6: Make the Payment
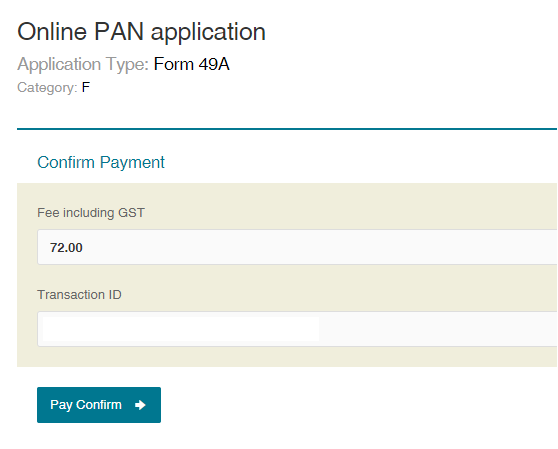
Step 7: You will be redirected to the bank site

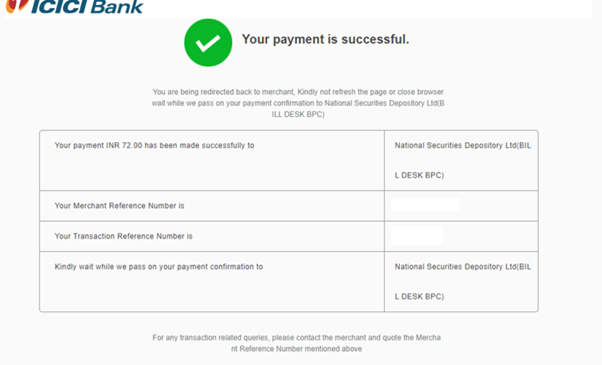
Step 8: Download the Payment Acknowledgment
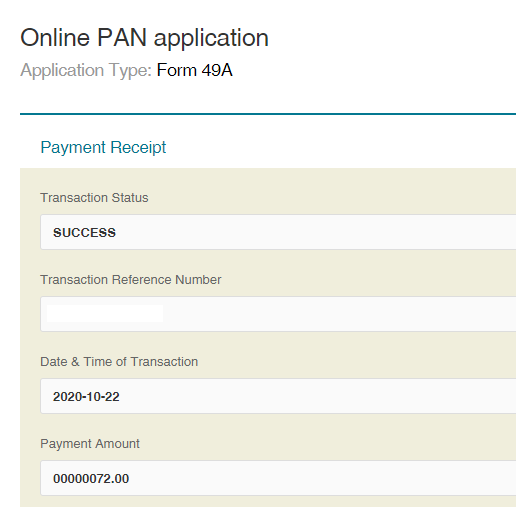
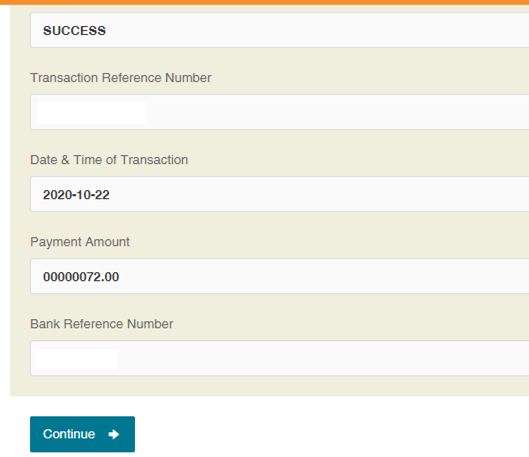
Step 9: Continue to download PAN Application
Step 10: Print PAN Application
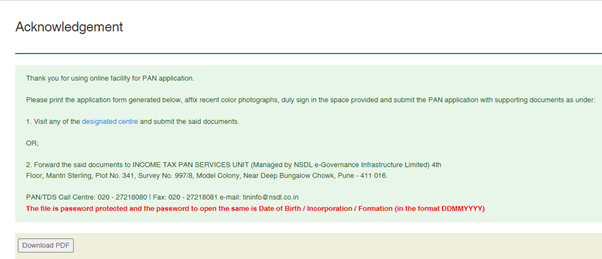
Step 11: Submit the signed application and documents to designated centres or post at:
INCOME TAX PAN SERVICES UNIT (Managed by NSDL e-Governance Infrastructure Limited) 4th Floor, Mantri Sterling, Plot No. 341, Survey No. 997/8, Model Colony, Near Deep Bungalow Chowk, Pune – 411 016
PAN/TDS Call Centre: 020 – 27218080 |Fax: 020 – 27218081
e-mail: tininfo@nsdl.co.in
14. How to Change the Citizenship Flag in PAN?
Facts
Mr A, while applying for the India PAN, mistakenly chose himself as an Indian citizen, whereas he is a citizen of the USA. Now, he wants to update his Citizenship with the Indian Tax Authorities.
Resolution 1: File an offline application with AO
There is no online procedure to change the citizenship in PAN records. An application must be made to the Assessing Officer having current jurisdiction over the PAN.
The assessee can approach the Assessing Officer in the following manner:
(a) Find the Jurisdictional Assessing Officer.
(b) Submit a letter to the Assessing Officer for change in Citizenship. Refer to the specimen of the letter to be submitted to the Assessing Officer.
Resolution 2: Submit the grievance
Mr A can choose to file a grievance on the e-filing portal. To submit the grievance, the assessee shall log in to the e-portal and submit a grievance to the concerned authority with relevant documents and a description of the grievance.
After submitting the grievance, Mr A can check the status of his grievance, which can be either of the following:
- Pending: In this case, the taxpayer is required to wait.
- Has Been Resolved.
- Has Been Transferred to AO: In this case, the taxpayer must visit the jurisdictional assessing officer to resolve the grievance.
- Pending for Documents: The department can always ask the assessee to submit the necessary documents to verify the assessee’s claim. These documents might be required to be uploaded to the e-filing portal or asked to be sent by post.
15. How to submit a Grievance if Aadhaar cannot be linked with PAN?
The Income Tax Department has launched a facility to submit grievances to the AO or various departments through the e-filing portal. The new e-filing portal has been enabled to receive and address all such grievances under a single window.
A taxpayer can submit the grievance to the following departments:
(a) e-filing
This department deals with the e-Filing of Income Tax Return or Statutory Forms and other value-added services like e-verification & e-proceedings. Grievances related to e-filing portal registration, profile or password, verification of ITR/Forms, e-proceedings, Instant PAN (e-PAN) through Aadhar, or Cybercrime (related to income tax) shall be logged under this department.
(b) Assessing Officer
Assessing Officers are designated income tax officers who handle the assessment of taxpayers under their jurisdiction and can be contacted for ITR-related specific queries. Grievances related to Refund, Rectification, Demand correction, Appeal order, PAN-related application, or any other miscellaneous application pending with AO shall be filed to the Assessing Officer.
(c) CPC-TDS
This department is associated with the e-TDS scheme. Any grievance related to portal access/registration, processing of TDS statements, Defaults, Challan/BIN corrections, Form 26AS, Form 16/27D, TDS Refunds, and TDS on the Sale of property shall be logged under this department.
(d) UTIITSL
This department deals with the issuance of PAN/ TAN and related queries. Any grievances related to Discrepancies/Errors in PAN application, Allotment of the same PAN to multiple entities, Logistics (Delivery of PAN card), or Aadhar Seeding shall be logged under this department.
(e) NSDL
This department deals with the issuance of PAN and related queries. Any grievances related to Rejected/Pending PAN applications, Discrepancies/Errors in PAN applications, Allotment of the same PAN to multiple entities, Logistics (Delivery of PAN card), or Aadhar Seeding shall be logged under this department.
(f) CPC-ITR
This department handles Income Tax Returns processing. All grievances related to ITR-V status, Intimations or Notices u/s 139(9) or 143(1), Refund not received, Income Tax Processing Related processes, Social Media grievances, or Feedback shall be logged under this department.
(g) SBI
This department deals with issuing tax refunds to the taxpayer post-ITR processing. Any grievances related to Refund Failed, Refund credited in the wrong account, and Refund paid but not credited in the account shall be logged under this department.
(h) DIT(Systems)
This department manages Information Technology-related systems in the Income Tax department. Any technical issues in the e-Filing website, PAN-related, Tax payment system (OLTAS), Escalation on existing Refund Banker (SBI) issues, Assessment, and Information mismatch shall be logged under this department.
For submitting the grievance if Aadhaar cannot be linked with PAN, the following steps will be followed:
Steps to Submit Grievance
Step 1: Visit https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal
Step 2: Log in using your registered PAN and password.
Step 3: Go to Grievances>Submit Grievance.
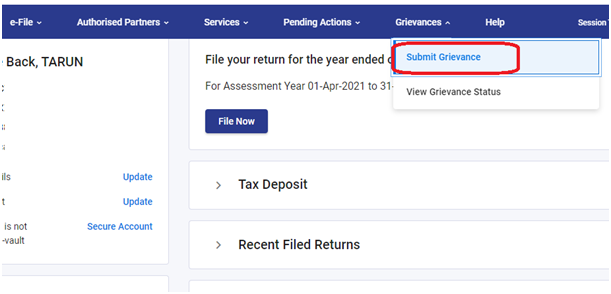
Step 4: You will be redirected to the ‘Submit a Grievance’ page. Select the relevant department with which the grievance is to be submitted
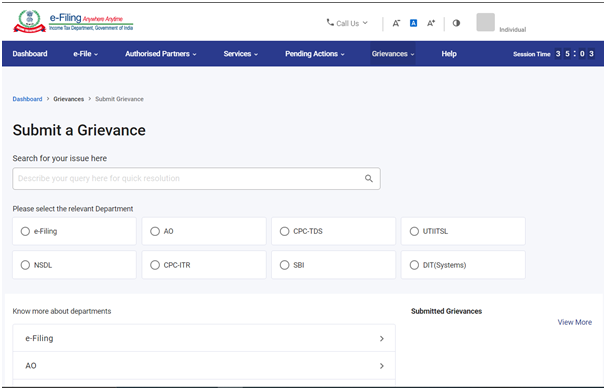
Step 5: After selecting the relevant department, select the category and sub-category of grievance from the dropdown list and click on ‘Continue’.
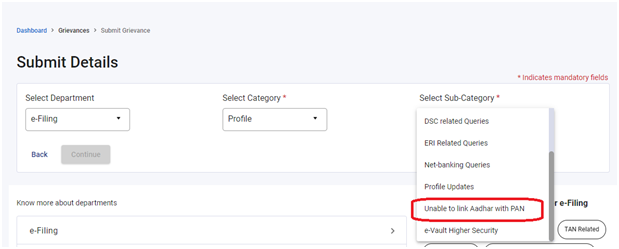
Refer to the snapshot below to check the details required to be filled in while filing a grievance if Aadhaar cannot be linked with PAN. The assessee can also upload the files from the given list or other documents. Upload the file by clicking on ‘Upload Attachment’ and click ‘Submit Grievance’ for submission.
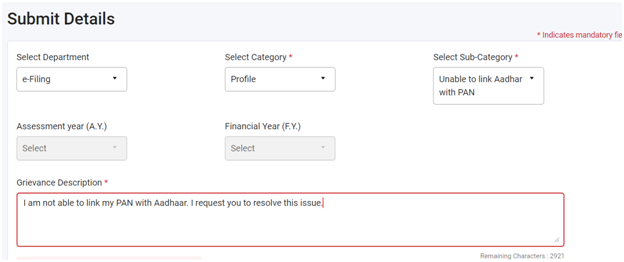
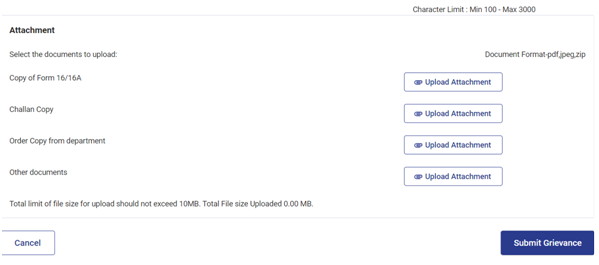
The grievance will be submitted, and an acknowledgement of submission will be displayed on the screen.
16. Why is PAN Card Important?
Here are some essential reasons why obtaining a PAN card is important:
- Legal Identity Verification:The PAN card is a valid identity proof with a photograph for various purposes, such as getting a gas connection or opening a bank account.
- Banking Transactions:A PAN card is necessary to open a bank account and conduct various financial activities. It helps combat fraud and money laundering. Cash deposits exceeding Rs. 50,000 in a day and fixed deposits over Rs. 50,000 require PAN card details.
- Debit/Credit Card Applications:PAN information is crucial when applying for debit or credit cards. Lack of PAN information or other factors leading to application rejection can negatively impact your credit score.
- Loan Applications: PAN card information is required for all types of loan applications.
- Property Transactions:For property transactions exceeding Rs. 5 lakhs, both the buyers and sellers must provide their PAN card details. In the case of joint ownership, all owners’ PAN card numbers are necessary.
- Purchasing Jewellery:PAN details must be submitted when purchasing jewellery or bullion worth more than Rs. 5 lakhs.
- Post Office Deposits: PAN information is required when opening Post Office deposits exceeding Rs. 50,000.
- Digital Payment Wallets:PAN card details are needed for monthly transactions above Rs. 20,000 in digital payment wallets.
- Vehicle Purchases: PAN card information is required for all vehicle sales or purchases except for two-wheelers.
- Share Trading:PAN card details are essential for share trading accounts, brokers, and Demat providers.
- Mutual Funds and Investments: PAN card information is necessary for investing in bonds, debentures, and mutual funds.
- Insurance Premiums: PAN card details are mandatory if your insurance premiums exceed Rs. 50,000 in a fiscal year.
- Foreign Currency Exchange:PAN card information is necessary for currency exchange involving local and foreign currencies.
- Employment and Tax Filing:Most workplaces require your PAN card information for salary accounting, tax purposes, and filing an Income Tax Return (ITR).
17. Benefits of PAN Card
Here are the key reasons why obtaining a PAN card is essential:
- Income Tax Returns Filing:Individuals and entities eligible for Income Tax must file their returns, and a PAN card is a prerequisite for this process. Hence, many individuals and entities apply for a PAN card.
- Identity Proof:The PAN card is a valid identity proof, widely accepted by financial institutions and other organizations besides the voter card and Aadhaar card.
- Tax Deductions:A PAN card is crucial for taxation purposes. If an individual or entity fails to link their PAN number with the bank account and their annual interest earnings on savings deposits exceed Rs. 10,000, the bank would deduct 30% TDS instead of 10%.
- Claiming Income Tax Refund:Sometimes, the TDS deducted from a taxpayer’s income exceeds the actual tax liability. To claim the excess tax paid, the taxpayer must have a PAN linked to their bank account.
- Starting a Business:Any entity, such as a company planning to start a business, must have a PAN registered in its name. The Tax Registration Number (TRN) required for a business is obtained only if the entity has a PAN.
18. FAQs
The department has issued the following FAQs in respect of instant e-PAN service.
FAQ 1: I have a PAN, but I have lost it. Can I get a new e-PAN through Aadhaar?
No. This service can only be used if you do not have a PAN but have a valid Aadhaar and your KYC details are updated.
FAQ 2: Are there any charges/fees for e-PAN?
No. It is completely free of cost.
FAQ 3: Who can apply for Instant e-PAN through Aadhaar?
PAN applicants who have an Aadhaar number from UIDAI and have linked their mobile number with Aadhaar can apply for instant e-PAN.
FAQ 4: What documents do I require for the new e-PAN?
You only require a valid Aadhaar with updated KYC details and a valid mobile number linked with your Aadhaar.
FAQ 5: Why do I need to generate an e-PAN?
It is mandatory to quote your Permanent Account Number (PAN) while filing your Income Tax Return. If you have not been allotted a PAN, you can generate your e-PAN with the help of your Aadhaar and a mobile number registered with your Aadhaar. Generating e-PAN is free of cost, an online process, and does not require filling out any forms.
FAQ 6: The current status of my PAN allotment request is updated as – PAN allotment request has failed. What should I do?
In case of failure of your e-PAN allotment, you may write to epan@incometax.gov.in.
FAQ 7: How will I know my e-PAN generation request has been submitted successfully?
A success message will be displayed along with an Acknowledgement ID. Please keep a note of the Acknowledgement ID for future reference. Additionally, you will receive a copy of the Acknowledgement ID on your mobile number registered with Aadhaar.
FAQ 8: I am unable to update my Date of Birth in my e-PAN. What should I do?
If only the year of birth is available in your Aadhaar, you will have to update the date of birth in your Aadhaar and try again.
FAQ 9: Can foreign citizens apply for PAN through e-KYC mode?
No.
FAQ 10: What should I do if my Aadhaar authentication gets rejected during e-KYC?
Aadhaar authentication may get rejected due to using the wrong OTP. The problem can be resolved by entering the correct OTP. If it still gets rejected, you have to contact UIDAI.
FAQ 11: Do I need to submit a physical copy of the KYC application or proof of the Aadhaar card?
No. This is an online process. No paperwork is required.
FAQ 12: Do I need to upload a scanned photo, signature, etc., for e-KYC?
No.
FAQ 13: Do I need to do in-person verification (IPV)?
No. The process is completely online. You do not need to visit any centre.
FAQ 14: Will I get a physical PAN card?
No. You will be issued an e-PAN which is a valid form of PAN.
FAQ 15: How do I get a physical PAN card?
If a PAN has been allotted, you can get a printed physical PAN card by submitting a request through the links below:
- https://www.onlineservices.nsdl.com/paam/ReprintEPan.html
- https://www.pan.utiitsl.com/PAN/reprint.html
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied







 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
