Liberalised Foreign Remittances Scheme (LRS) | Law & Procedure
- Blog|Income Tax|
- 20 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 11 October, 2023

Table of Contents
- Brief Overview of Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS)
- Understanding Current & Capital Account Transactions
- Permissible Current Account Transactions
- Permissible Capital Account Transactions
- Procedure for Remittance under LRS
- Tax Collection at Source (TCS) on Foreign Remittances under LRS
- Case Studies
1. Brief Overview of Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS)
1.1 Background
- Prior to introduction of the LRS, drawl of foreign exchange by RI was governed by Current Account Transaction (CAT) Rules, 2000 divided under three schedules as follows:
| Schedule I | Completely prohibited transactions |
| Schedule II | Remittances allowed only with the prior approval of the concerned Ministry of the Central Government |
| Schedule III | Permissible transactions. Limits prescribed for certain transactions beyond which procedures/approvals are prescribed. |
- There were no restriction or limit on other Current Account Transaction which were not covered by any of the above mentioned three schedules (ADMA Cir. No. 11 dated 4.05.2000)
- For Capital Account Transactions, remittances were governed by independent Capital Account Notifications issued for permissible capital account transactions.
1.2 Liberalized Remittance Scheme (‘LRS’)
- LRS was introduced on February 4, 2004, with a initial limit of USD 25,000 per financial year
- LRS brought in as a measure of partial capital account convertibility by allowing remittances for current or capital account transactions or combination of LRS was originally to be allowed in addition to various limits prescribed under Schedule III for certain Current Account Transactions by RIs.
- Vide AP Dir. Circular 24 dated December 20.2006 facilitates under (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000 were subsumed under LRS. All facilities for release of foreign exchange for RI under Para 1 of Schedule III, as amended from time to time, for current account transactions will now be under overall LRS limit.
- Similarly, until clarifications by RBI vide AP Dir. Circular 24/Notification No. 282 both dated 14th August, 2013 and Notification FEMA 263/RB-2013 dated August 5, 2013, it was perceived that remittances for specified Capital Account Transactions was allowed freely irrespective of absence of specific provisions under various Capital Account Notifications including incorporation of an entity outside India for strategic purposes.
- Limit has increased over the years (except reduction between August 2013 till May, 2015 due to depleting forex reserves). Remittances from EEFC/RFC to be also considered within LRS ceiling
| Amount US $ | |||||||
| Date | Feb 4, 2004 | Dec 20, 2006 | May 8, 2007 | Sept 26, 2007 | Aug14, 2013 | June 3, 2014 | May 26, 2015 |
| LRS Limit | 25,000 | 50,000 | 1,00,000 | 2,00,000 | 75,000 | 125,000 | 2,50,000 |
- The Scheme is available to all RIs including
- Remittances under the Scheme can be consolidated in respect of family members. However, clubbing is not permitted by other family members for capital account transactions such as opening a bank account/investment, etc., if they are not the co- owners/co-partners of the overseas bank account/investment,
- RI cannot gift to another RI in foreign currency, for the credit of the latter’s foreign currency account held abroad under LRS.
- Payment by International credit card was sought to be brought under the limit of LRS vide e-gazette notification dated 16th May, Vide Press release dated 28th June, 2023, the classification of use of international credit card while being overseas will be outside the LRS till 30.09.2023. As a consequence restrictions of LRS limit and provisions of TCS contained in Section 206C(1G) will not apply on such payments till 1.10.2023.
1.3 Remittance Prohibited under LRS
- Remittance for any purpose specifically prohibited under Schedule-I (like purchase of lottery tickets/sweep stakes, proscribed magazines, etc.) or any item restricted under Schedule II of Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000.
- Remittances for transactions not permissible under FEMA and those in the nature of remittance for margins or margin calls to overseas exchanges/ overseas counterparty are not allowed under the Scheme
- Remittances for purchase of Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCB) issued by Indian companies in the overseas secondary market.
- Remittance for trading in foreign exchange abroad.
- Capital account remittances, directly or indirectly, to countries identified by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) as “non-cooperative countries and territories”, from time to time.
- Remittances directly or indirectly to those individuals and entities identified as posing significant risk of committing acts of terrorism as advised separately by the Reserve Bank to the banks.
2. Understanding Current & Capital Account Transactions
2.1 Current And Capital Account Transactions
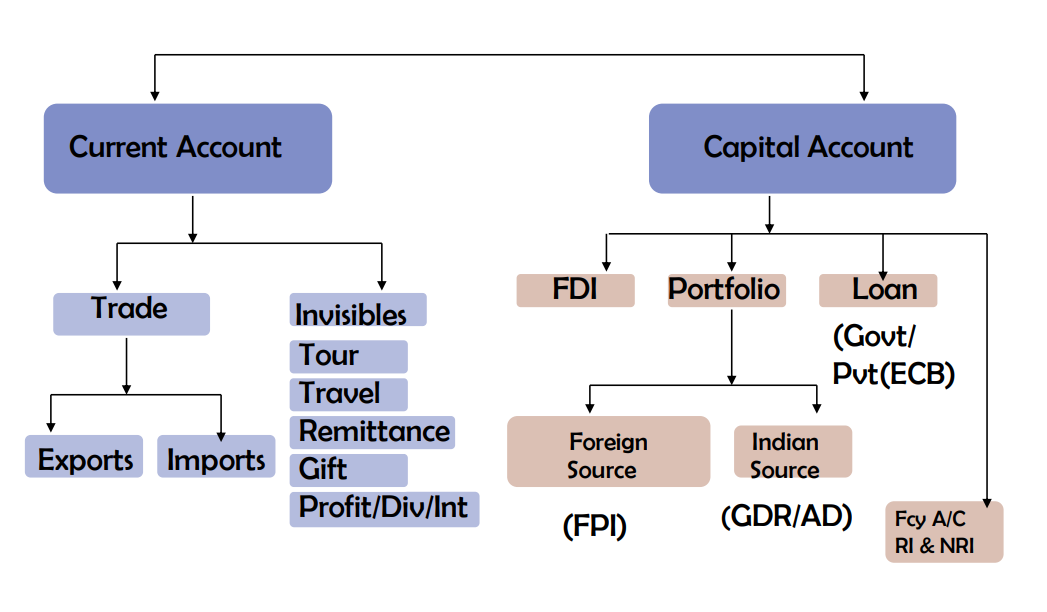
2.2 Definitions
2.2.1 Capital Account Transactions
2(e) “capital account transaction” means a transaction which alters the assets or liabilities, including contingent liabilities, outside India of persons resident in India or assets or liabilities in India of persons resident outside India, and includes transactions referred to in sub- section (3) of section 6
2.2.2 Current Account Transactions
2(j) “current account transaction” means a transaction other than a capital account transaction and without prejudice to the generality of the foregoing such transaction includes-
- payments due in connection with foreign trade, other current business, services, and short-term banking and credit facilities in the ordinary course of business,
- payments due as interest on loans and as net income from investments,
- remittances for living expenses of parents, spouse and children residing abroad, and
- expenses in connection with foreign travel, education and medical care of parents, spouse and children
2.3 Permissible Transactions
| Current Account Transactions | Capital Account Transactions |
| i. Private visits to any country (except Nepal and Bhutan).
ii. Gift or donation. iii. Going abroad for employment. iv. Emigration.* v. Maintenance of close relatives abroad. vi. Travel for business, or attending a conference or specialized training or for meeting expenses for meeting medical expenses, or check-up abroad, or for accompanying as attendant to a patient going abroad for medical treatment/ check-up. vii. Expenses in connection with medical treatment abroad. * viii. Studies abroad.* ix. Any other current account transaction |
i. Opening of foreign currency account abroad with a bank.
ii. Acquisition of immovable property abroad- Rule 21 of Overseas Investment Rules, 2022. iii. Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) and Overseas Portfolio Investment (OPI) abroad (In accordance with Rule 13- Schedule –III of Overseas Investment Rules, 2022.) iv. Extending loans including loans in Indian Rupees to Non-resident Indians (NRIs) who are relatives as defined in Companies Act, 2013. |
* Resident Individuals Can Avail Exchange Facility Under These Categories in Excess of Us $ 2,50,000 if It Is So Required by the Country of Emigration, Medical Institute Offering The Treatment or the University Respectively.
3. Permissible Current Account Transactions
3.1 Private Visits/Gifts/Donations/Employment
Private visits abroad
- For private visits abroad, other than to Nepal and Bhutan, any resident individual can obtain foreign exchange up to an aggregate amount of USD 2,50,000 from an AD or FFMC, in a financial year, irrespective of the number of visits undertaken during the year.
- Further, all tour related expenses including cost of rail/road/water transportation; cost of Euro Rail; passes/tickets, etc. outside India; and overseas hotel/lodging expenses shall be subsumed under the LRS limit. The tour operator can collect this amount either in Indian rupees or in foreign currency from the resident traveler.
Gift/donation
- RI can remit within LRS limit of USD 2,50,000 in one FY as gift to a person residing outside India or as donation to an organization outside India.
- Gift in rupee shall be by way of crossed cheque/electronic transfer and should be credited to the NRO account of the NRI/PIO. Gift in rupees will also be under the LRS limits.
Going abroad on employment
- A person going abroad for employment can draw foreign exchange up to USD 2,50,000 per FY from any Authorised Dealer in India
3.2 Emigration/Maintenance of Close Relatives/Business Trip
Emigration
- A person wanting to emigrate can draw foreign exchange from AD Bank up to the amount prescribed by the country of emigration or USD 250,000.
- Remittance of any amount of foreign exchange in excess of this limit can be allowed only towards meeting incidental expenses in the country of immigration and not for earning points or credits to become eligible for immigration by way of overseas investments in government bonds; land; commercial enterprise; etc.
Maintenance of close relatives abroad
- A resident individual can remit up-to USD 2,50,000 per FY towards maintenance of close relatives [‘relative’ as defined in Section 2(77) of the Companies Act, 20137 abroad.]
Business Trip
- Visits by individuals in connection with attending international conference, seminar, specialised training, apprentice training, etc., are treated as business visits. The amount can be spent within the overall limit of USD 2,50,000 irrespective of number of visits abroad.
- However, when an employee is deputed by an entity for any of the above purposes and the expenses are borne by the entity, such expenses shall be treated as residual current account transaction outside LRS and may be permitted by the AD without any limit, subject to verifying the bonafides of the transaction.
3.3 Medical Treatment/Student Studying Abroad
Medical treatment abroad
- AD may release foreign exchange up to an amount of USD 2,50,000 or its equivalent per FY without insisting on any estimate from a hospital/doctor.
- For any amount exceeding the above limit, AD may release foreign exchange under general permission based on the estimate from the doctor in India or hospital/ doctor abroad. A person who has fallen sick after proceeding abroad may also be released foreign exchange by the AD (without seeking prior approval of the RBI) for medical treatment outside India.
- In addition to the above, drawal up to USD 250,000 per financial year is allowed to a person for accompanying as attendant to the patient going abroad for medical treatment/check-up under this category.
Students studying abroad
- AD may release foreign exchange to resident individuals for studies abroad up to USD 2,50,000 or its equivalent without insisting on any estimate from foreign University.
- However, AD may allow remittances exceeding USD 2,50,000 (without seeking prior approval of RBI) based on the estimate received from the education institution abroad.
3.4 Permissible Current Account Transactions
Other Points
- Remittances under the Scheme can be used for purchasing objects of art subject to the provisions of other applicable laws such as the extant Foreign Trade Policy of the Government of India.
- The Scheme can be used for outward remittance in the form of a DD either in the resident individual’s own name or in the name of beneficiary with whom he intends putting through the permissible transactions at the time of private visit abroad, against self-declaration of the remitter in the format prescribed. (Form A2 with LRS Declaration).
- Banks should not extend any kind of credit facilities to facilitate capital account remittances under the Scheme.
4. Permissible Capital Account Transactions
4.1 Opening foreign currency account with a bank abroad/Acquisition of Immovable property abroad
Opening of foreign currency account abroad with a bank
- Individuals can also open, maintain and hold foreign currency accounts with a bank outside India for making remittances under the Scheme without prior approval of the Reserve Bank. The foreign currency accounts may be used for putting through all transactions connected with or arising from remittances eligible under this Scheme.
- The unspent/unused foreign exchange, unless invested/ reinvested, shall be repatriated and surrendered to an AD in India within a period of 180 days. This will also apply to income earned overseas on LRS investments, unless reinvested within the stipulated period. (Para -16 – Master Direction dated January 1, 2016, updated up to 24th August, 2022.
Acquisition of immovable property abroad- Rule 21 of Overseas Investment Rules,
- In terms of Rule 21(2), a person resident in India is allowed to acquire immovable property outside India by way of purchase out of the remittances sent under the LRS.
- Such remittances under the LRS can be consolidated in respect of relative(s), if such relatives, being person(s) resident in India, comply with the terms and conditions of the Scheme.
4.2 Family Members – Clubbing
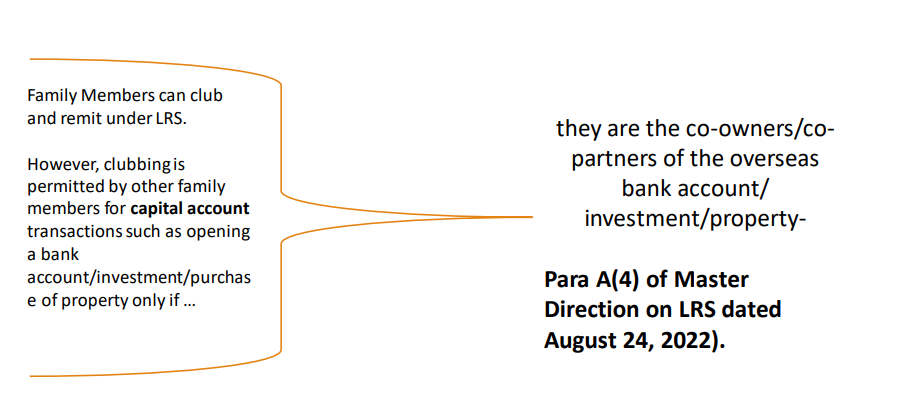
A resident cannot gift to another resident, in foreign currency for the credit of the latter’s foreign currency account held abroad under LRS. Therefore, such investment should be in joint names and held in proportion to the amount remitted under the LRS.
4.3 ODI under LRS
(In accordance with Rule 13- Schedule III of Overseas Investment Rules)
Overseas Direct Investment by RI (ODI):
“Overseas Direct Investment” or “ODI” means investment by way of acquisition of unlisted equity capital of a foreign entity, or subscription as a part of the memorandum of association of a foreign entity, or investment in ten per cent, or more of the paid-up equity capital of a listed foreign entity or investment with control where investment is less than ten per cent. of the paid-up equity capital of a listed foreign entity;
Conditions
- ODI is in an ‘operating foreign entity’ not engaged in ‘financial services activity’
- Exception: Shares acquired as sweat equity, ESOP of minimum qualification shares for holding management post.
- Acquisition through subscription as part of MOA or purchase of equity capital, listed or unlisted and subsequent rights/bonus.
- The entity does not have subsidiary or step down subsidiary where the resident individual has control in the foreign entity.
- (v) “subsidiary”/ “step down subsidiary (SDS)” of a foreign entity means an entity in which the foreign entity has control and the structure of such subsidiary/SDS shall comply with the structural requirements of a foreign entity, i.e., such subsidiary/SDS shall also have limited liability where the foreign entity’s core activity is not in strategic sector. The investee entities of the foreign entity where such foreign entity does not have control (as defined above) shall not be treated as SDSs and therefore need not be reported henceforth.
- “control” means the right to appoint majority of the directors or to control management or policy decisions exercisable by a person or persons acting individually or in concert, directly or indirectly, including by virtue of their shareholding or management rights or shareholders’ agreements or voting agreements that entitle them to ten per cent. or more of voting rights or in any other manner in the entity [Rule 2(c)]
- Where a resident individual has made ODI without control in a foreign entity that subsequently acquires or sets – up a subsidiary/SDS, such resident individual shall not acquire control in such foreign entity. [Overseas Investment Directions – Para 22(1)]
Overseas Direct Investment by RI (Purpose Code S0003) (ODI)
- Investment in the form of equity or personal guarantees. Investment by way of loan is not allowed.
- Acquisition of less than ten per cent. of the equity capital, whether listed or unlisted, of a foreign entity without control where shares acquired as sweat equity, ESOP of minimum qualification shares for holding management post) shall be treated as OPI
- If amounts to “control” even acquisition of 1 share will amount to ODI and will not be considered as OPI.
- Capitalisation, within the time period, if any, specified for realization, of any amount due from the foreign entity the remittance of which is permitted under the Act or does not require prior permission of the CG/RBI.
- Investment – Valuation to be at arm’s length basis
- Investment from EEFC/RFC also included within LRS ceiling.
Obligations
- Obtain UIN
- Submit share certificate/other evidence within 6 months
- Repatriate dues within 90 days of their becoming due
- Incorporation of timeline in MOA in case of deferred consideration
- NOC for NPA Account/Wilful defaulter accounts
Overseas Portfolio Investment by RI (OPI)
- “Overseas Portfolio Investment” or “OPI” means investment, other than ODI, in foreign securities, but not in any unlisted debt instruments or any security issued by a person resident in India who is not in an IFSC
- OPI by a person resident in India in the equity capital of a listed entity, even after its delisting shall continue to be treated as OPI until any further investment is made in the entity.
RI can make OPI (Purpose Code: S0001) in the manner provided in Schedule –III of Overseas Investment Rules, 2022, subject to LRS ceiling by way of
- Reinvestment of earnings ( i.e. income earned on LRS investments overseas)
- Capitalisation of permissible dues which does not require prior permission of RBI
- Swap of securities on account of a merger, demerger, amalgamation or liquidation;
- Acquisition of equity capital through rights issue or allotment of bonus shares;
- Gift as per the conditions laid down under this Schedule;
- Inheritance;
- Acquisition of less than ten per cent. of the equity capital, whether listed or unlisted, of a foreign entity without control by way of
- Sweat equity shares;
- Minimum qualification shares issued for holding a management post in a foreign entity;
- Acquisition of shares or interest under Employee Stock Ownership Plan or Employee Benefits Scheme.
4.4 Extending Loan to relatives abroad
- RI can to lend to a NRI/ PIO relative [as defined in Section 2(77) of the Companies Act,
2013] subject to the following conditions:- the loan is free of interest and the minimum maturity of the loan is one year;
- the loan amount shall be within the overall limit under the LRS of USD 2,50,000 per FY
- the loan shall be utilized for meeting the borrower’s personal requirements/ own business purposes in India.
- the loan shall not be utilized, either singly or in association with other person for any of the activities in which investment by persons resident outside India is prohibited, namely:
- The business of chit fund, or
- Nidhi Company, or
- Agricultural or plantation activities or in real estate business, or construction of farm houses, or
- Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDRs).
- For this purpose real estate business shall not include development of townships, construction of residential/commercial premises, roads or bridges.
- the loan amount should be credited to the NRO account of the NRI/PIO. Credit of such loan amount may be treated as an eligible credit to NRO account;
- the loan amount shall not be remitted outside India; and
- repayment of loan shall be made by way of inward remittances through normal banking channels or by debit to NRO/NRE/FCNR/sale proceeds of the shares or securities or immovable property against which such loan was granted.
4.5 Other Points
Soliciting deposits
- All banks, both Indian and foreign, including those not having an operational presence in India, should seek prior approval from RBI for the schemes being marketed by them in India to residents either for soliciting foreign currency deposits for their foreign/overseas branches or for acting as agents for overseas mutual funds or any other foreign financial services company.
Retain/Re-invest
- Investor, who has remitted funds under LRS can retain, reinvest the income earned on the investments subject to ODI provisions.
- Unspent/unused foreign exchange lying in a bank account abroad, unless reinvested, shall be repatriated and surrendered to an authorised person within a period of 180 days from the date of such receipt/realisation/ purchase/acquisition or date of return to India, as the case may be,
- Notification 1(R)/Regulation 3 allows retention up to USD 2,000 retention of unspent forex beyond 180 days.
4.6 Remittances to International Financial Service Centre (IFSC)
- The remittance shall be made only for making investments in IFSCs in securities, other
than those issued by entities/companies resident (outside IFSC) in India. - RI allowed to open a non interest bearing Foreign Currency Account (FCA) in IFSCs, for
making the above permissible investments under LRS. - RI is not allowed to settle any domestic transactions with other residents through FCAs held in IFSC.
- AP can allow remittances under purpose ‘studies abroad’ as mentioned in Schedule III of
Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000 for payment
of fees to foreign universities or foreign institutions in IFSCs. -A.P. (DIR Series) Circular
No. 06 dated 22 June, 2023
5. Procedure for Remittance under LRS
- RI to designate a branch of an AD Bank through which all the remittances under LRS will be made.
- The applicants should have maintained the bank account with AD for a minimum period of one year prior to the remittances for capital account transactions. If the applicant is a new customer, AD to carry out due diligence on the opening, operation and maintenance of the account.
- The applicant to declare that the total amount of foreign exchange purchased from or remitted through, all sources in India during the financial year including this application is within the overall limit of the LRS and certify that the source of funds for making the remittance belongs to him and the foreign exchange will not be used for prohibited purposes.
Document/Procedure for Remittance under LRS
- The applicant to declare that total amount of foreign exchange purchased from or remitted through, all sources in India during this calendar year including this application is within the annual LRS limit.
- AD to observe KYC Guidelines, Obtain Copy of PAN
- Furnish Form A2 containing beneficiary’s name, address, purpose code & LRS declaration.. In case of remittance under LRS by a minor, Form A2 must be countersigned by the natural guardian.
- RBI will not, generally, prescribe the documents which should be verified by the Authorised Persons while releasing foreign exchange for current account transactions.
- In terms of sub-section (5) of Section 10 of the FEMA, 1999, AP shall require any person desiring to transact in foreign exchange to make such a declaration and to give such information as will reasonably satisfy him that the transaction will not involve and is not designed for the purpose of any contravention or evasion of the provisions of the FEMA or any rule, regulation, notification, direction or order issued there under.
- AD, in order to maintain uniformity, may consider requirements or documents to be obtained by their branches to ensure compliance with provisions of sub-section (5) of section 10 of the Act.
- AD shall certify that the remittance is directly or indirectly not made by /or to ineligible entities and that the remittance is in conformity with the instructions issued by RBI from time to time under the Scheme
6. Tax Collection at Source (TCS) on Foreign Remittances under LRS
- TCS provision on Foreign remittances under LRS were introduced effective from 1st October, 2020.
- AD to collect TCS from Buyer (Remitter/buyer of overseas tour package)
- Time of TCS Collection –
- At the time of receipt of remittance amount by AD by any mode from the buyer, or
- At the time of debiting the amount payable by the buyer, whichever is earlier
Exclusions for the applicability of Section 206C (1G) –
-
- Central Government, State Government, an embassy, a High Commission, legation, commission, consulate, and the trade representation of a foreign State.
- A local authority as defined in Section 10(20) of the Act.
- Any person specified by the Central Government through a notification in the Official Gazette.
- TCS is not applicable if the overseas remittance under LRS is subject to TDS and the customer makes TDS.
- Transfer to NRO Account as Gift
- Public sector undertakings, government companies are not excluded.
- TCS can be claimed as credit against tax payable in the ITR – TCS amount to appear in Form 26AS.
- TCS is not applicable on foreign remittances which are not covered under the LRS.
- Certain changes proposed by the Finance Act, 2023 deferred till 30.09.2023 and new rates prescribed vide Press Note dated 28th June, 2023.
|
Modified rate effective from 1.07.2023 till 30.09.2023 |
New Rate from 01.10.2023 (On the presumption that rate notified by FA 2023 will apply including threshold for category 4) |
||||
| S. No. | Particulars | If PAN is Available | If PAN is not Available | If PAN is Available | If PAN is not Available |
| 1 | LRS – For Education financed by loan Code: S0305 | NIL up to Rs. 7.00 Lakhs 0.5% above Rs. 7.00 Lacs | NIL up to Rs. 7.00 Lakhs 10.00% above Rs. 7.00 Lacs | NIL up to Rs. 7.00 Lakhs 0.5% above Rs. 7.00 Lacs | NIL up to Rs. 7.00 Lakhs 20.00% above Rs. 7.00 Lacs |
| 2 | LRS – For Medical Treatment and Education (Other than financed by loan) Code: S0304 |
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh
5% above Rs 7 Lakh |
NIL up to Rs. 7.00 Lakhs
10.00% above Rs. 7.00 |
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh
5% above Rs 7 Lakh |
TCS @ 10% of Remittance Amount in excess of Rs. 7.00 Lacs |
| 3 | LRS for other purposes | Nil up to Rs 7 lakh
5% above Rs 7 Lakh |
NIL up to Rs. 7.00 Lakhs
10.00% of the amount in excess of Rs. 7.00 Lacs |
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh
20% above Rs 7 Lakh |
TCS @ 40% of the remittance amount |
| 4 | Overseas Tour Program (Payment for Purchase of Ticket, Booking Hotel, etc.) Code:S0306 | Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 Lakh (Threshold for this category is to apply independently
Note: There was no threshold exemption till 30.06.2023 |
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 10% above Rs 7 Lakh (Threshold for this category is to apply independently
Note: There was no threshold exemption till 30.06.2023 |
5% till Rs. 7 Lakhs
20% above Rs. 7 Lakhs (Note: This threshold to apply indepdently) |
5% till Rs. 7 Lakhs
40% above Rs. 7 Lakhs (Note: This threshold to apply indepdently) |
7. Case Studies
7.1 Case Study 1
Facts: Mr Rakesh Malhotra is a professional residing in Mumbai. He wants to make certain remittances outside India under LRS for which he seeks your advice on the amount that he and his wife can draw foreign exchange and TCS implication thereon:
| Issue | Comments | TCS Implications |
|
|
Upto 30.09.2023
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 Lakh From 1.10..2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 20% above Rs 7 Lakh |
|
|
Upto 30.09.2023
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 Lakh From 1.10..2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 20% above Rs 7 Lakh |
7.2 Case Study 2
Facts: Mr Achyut, son of Mr Vijay Singh, a wealthy businessman, is going to USA for further studies after completion of his graduation in India. The cost of his education is estimated to be USD 2,00,000 which Mr Vijay wants to remit from his own funds to his son’s account in USA by way of Gift. Mr Vijay is a partner of M/s. Vijay Sales and therefore wants to travel with his son for promotion of his business. His wife Ms. Lina will join for a pleasure trip. His mother Mrs Sujata will travel for medical treatment for which hospital has provided estimate of USD 300,000. He needs your advice on the amount of forex and the best possible compliant manner that they can draw required forex.
| Purpose | Amount under LRS | Comments | |
| Mr. Achyut’s Education. Cost | USD 200,000 |
|
Upto 30.09.2023
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 Lakh From 1.10..2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 20% above Rs 7 Lakh
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 0.5% above Rs 7 Lakh |
| Mr Vijay Singh’s Business Trip | NIL |
|
|
| Mrs Lina’s Pleasure Trip | Within LRS limit of USD 2,50,000 |
|
Upto 30.09.2023
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 Lakh |
| Mrs Sujata’s Medical treatment | As per LRS Scheme up to USD 2,50,000 + additional amount |
|
Draw exchange for other requirements and thereafter draw exchange for medical treatment based on the estimate |
7.3 Case Study 3
Facts: Mr Nari Chhabaria, a Businessman wants to open an account with a bank in UAE and remit his full LRS entitlement of USD 2,50,000 anticipating vide exchange fluctuation and imminent increase in TCS rates. He has plans to buy immovable property or make other portfolio investments but as of now has not firmed up any plan. He seeks your advice on this and the purpose code that he needs to fill in in his Form A2.
| Issue | Comments | TCS Implications |
|
|
Upto 30.09.2023
Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 Lakh
From 1.10..2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 20% above Rs 7 Lakh |
7.4 Case Study 4
Facts: The family of Mr. Pankit Mehta consists of 3 members including his wife and a daughter. He wants to buy a house in UAE and avail of the benefit of Golden Visa Scheme. The cost of the house is likely to be USD 7,00,000. The house will be used as and when family members visit UAE. Mr Pankit Mehta seeks your advice to achieve the goal in compliant manner.
Practical considerations-
Payment in instalments:
- The cost of property is USD 7,00,000. Financial commitment in one financial year cannot exceed LRS limit
- No clarity even when annual instalments due are within the LRS limit could construe as current account transaction.
- If construed as a capital account transaction, this would alter his liability outside India and is not specifically permitted under capital account regulations notified by the RBI/GOI.- Refer Section 2(e).
- AP Circular 32 dated 4.9.2013 which allowed payment in instalments within LRS was in respect of pre-existing contracts as of 14.8.2013. No such relaxation now
- Hence acquisition in instalments is not advisable
Housing Loans:
- RI are not allowed to obtain housing loans outside India as this would alter his liability outside India and is not specifically permitted under capital account regulations notified by the RBI/GOI.
Setting up an entity in UAE to acquire property:
- RI allowed to set up an entity for bonafide business purposes abroad. Investment in immovable property for personal use cannot construe bonafide business purpose outside India.
Joint Investment by family members
Conditions:
- Remittances under the Scheme can be consolidated in respect of family members subject to individual family members complying with terms and conditions under the LRS
- However, clubbing is not permitted by other family members for capital account transactions such as opening a bank account/investment, investment in immovable
property, etc. if they are not the co owners/co-partners of the overseas bank account/investment - Remittances for purchase of property shall be in accordance with the provisions under paragraph 6(ii). Further, a resident cannot gift to another resident, in foreign currency, for the credit of the latter’s foreign currency account held abroad under LRS.
- Therefore, Mr Pankit Mehta can buy the property in joint name of three family members with each member being joint owner of the property in the proportion of the payment made by them
Mr Pankit Mehta can evaluate this option and acquire the property in joint names off the family members.
7.5 Case Study 5
Facts: Mr Ketan Mehta wants to make following investments in his personal capacity –
- Investment of USD 5,000 for in an unlisted entity in Singapore for 5% stake in the equity capital of USD 100,000
- Portfolio investment of USD 50,000 through an investment bankers in various listed entities overseas
Kindly advice him about the regulatory position in India.
| Issue | Comments | TCS Implications |
| Investment of USD 5,000 for in an unlisted entity in Singapore for 5% stake in the equity capital of USD 100,000 |
|
Upto 30.09.2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 LakhFrom 1.10..2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 20% above Rs 7 Lakh |
| Portfolio investment of USD 50,000 through an investment bankers in various listed entities overseas |
|
Upto 30.09.2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 5% above Rs 7 LakhFrom 1.10..2023 Nil up to Rs 7 lakh 20% above Rs 7 Lakh |
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied





 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA

As per my understanding and knowledge, transfer to NRO account as gift or giving interest free loan to NRI/PIO by resident individual is permitted under FEMA subject to some conditions and the remitter has to make sure that all the remittances have not exceeded the LRS limit of USD 250,000 during a year. and TCS will be applicable on the same at the prescribed rate without any exemption limit.
However, in the above blog the concerned person has mentioned that the transfer to NRO account as gift is out the ambit of TCS applicability.
Need clarification on above concern.
Thanking in advance.
Waiting for a valuable response.