Guide to Forensic Auditing – Insights, Techniques, and Case Studies in Fraud Investigation
- Other Laws|Blog|
- 9 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 4 February, 2024

By Shrenik Shah – Founder & Partner | SN & Co.
Table of Contents
- What is Fraud?
- Classification of Fraud
- Conventional Approach v/s Forensic Approach
- Four Phase Fraud Cycle
- Types of Trigger
- Preventive Technique
- Practical Case Studies
- Digital Forensic – Walkthrough
- Interrogation Techniques
- Care to Cure
- Forensic – Prospects
- Directories
1. What is Fraud?
Universal Our Belief
Financial – Fair
Reward – Recovery
Acquired – Acquired
Under – Unfair
Deception – Doctrine
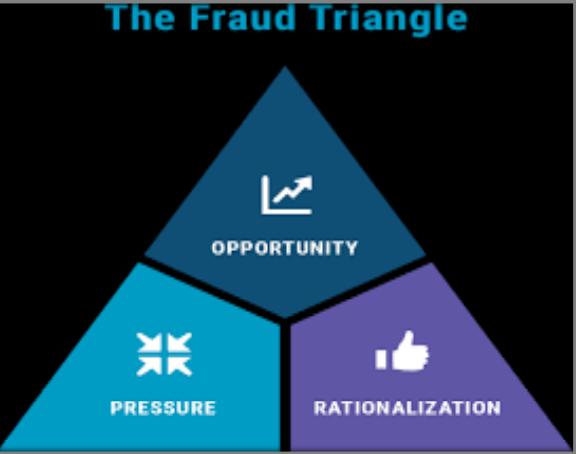
Maths on Fraud = MQ < (O + P) R
MQ – Moral Quotient = (W * IQ)
O – OPPORTUNITY,
P – Pressure,
R – Rationalisation
1.1 Separating Truth From Fiction: Unveiling the Common Myths of Forensic Audit
Fiction
- Only CA’s are capable to conduct financial fraud investigation
- Financial Frauds investigation happens only on financial records
- Forensic can be conducted by any tools & protocols
- Any and all Data Can Be Recovered In case of digital forensics
- Pressing whistle involves identity Risk
- Fraudster commits fraud as a One Day Affair
- Forensic Auditor can recover money from fraudster
- Once Forensic Report issued can’t be challenged
Facts
- Anyone with a skeptical eye can conduct an investigation with adequate credentials
- Fraud investigations extend beyond numbers i.e. Covert Operations, Social Media profiling
- The tools used for forensic shall be admissible in court of law
- When the storage medium is extremely damaged, this is not always possible
- There are numerous whiste-hotlines that help safeguarding whistleblower’s identity
- Fraudster commits fraud over a period of time encompassing a series of red flags
- Recovery of money invites legal attention
- Alleged -party can issue a counter report as well to question the forensic report
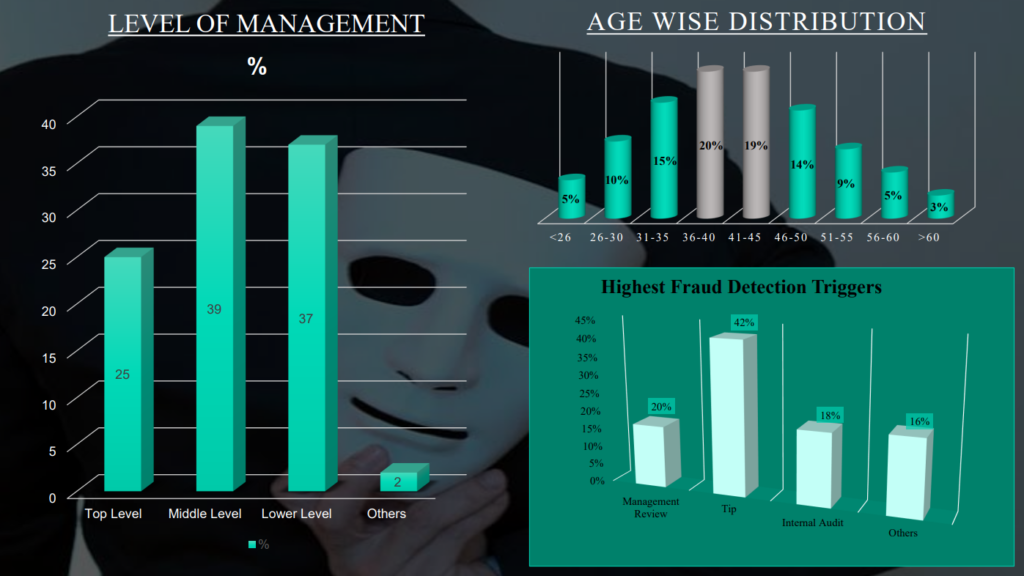
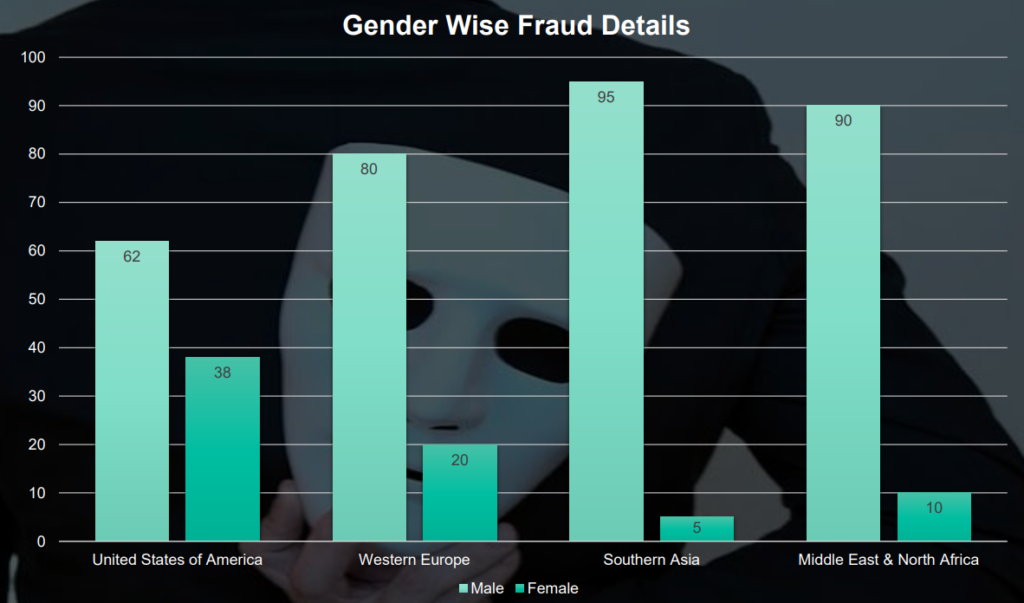
1.2 Statistics
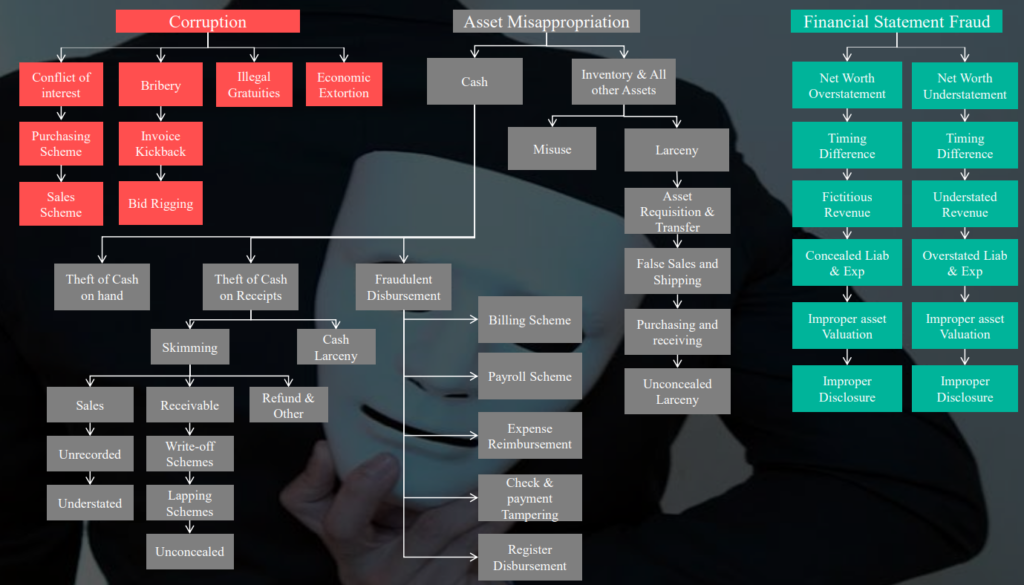
2. Classification of Fraud
3. Conventional Approach v/s Forensic Approach
Conventional Audit Approach
- Implementation and Testing of financial controls
- Overall risk assessment
- Ensuring compliance
- Financial Statement preparation
- Identification of process lapses
Forensic Approach
- Data mining with skeptical eye
- Deep Dive Approach to identify hidden frauds
- Red Flag Identification
- Pattern analysis
- 7 eye approach
3.1 Atypical Approach– 7 Eye Theory
Your Eye
- Skeptical Attitude
- Connecting Dots Perspective
- Investigative approach
Data Eye
- Data analytics – To identify duplications, irregularities, trends & patterns, Link Analysis, Joining Files, Fund Trail etc
Digital Eye
Digital Forensic is scanning of emails, hard disk, mobile phones and recovery of deleted files, password cracker & so on
Network Eye
- Market Intelligence
- Surveillance & Covert Operations
Evidence Eye
- Without Evidence entire exercise is futile
- Need to be proven in court of law
Theory Eye
- Gun Powder Theory
- Time Bomb Theory
- Inverse Logic Theory
- RSF Theory
- Benford’s Law Theory
Tool Eye
- Tools play an important role while using investigative techniques
- GST, Logistics Tracking Tool, Background Verification Tool etc.
4. Four Phase Fraud Cycle
Prevention
- Red Flag & Green Flag Identification & Monitoring
- Implementation & Testing of controls
- Vendor, Employee & Third Party Due Diligence – Scan Theory & Pyschometric Test
- Anti Fraud Framework
- Implementation of whistle blow & vigil mechanism
Detection
- Lifestyle & Background check
- Forensic examination of documents
- Tailing, Spying, Hacking & Screening, Social Media Profiling
- Digital Forensic
- Market research, Covert Uncovered Operation, pretext calling
- Vendor Vigilance
Correction
- Interrogation Techniques
- Indemnification Techniques
- Risk Appetite Redefinition
- Control Deficiency Correction
Reporting
- Compliance with legal, regulatory and other requirements
- Evidence
- Conclusion – Report
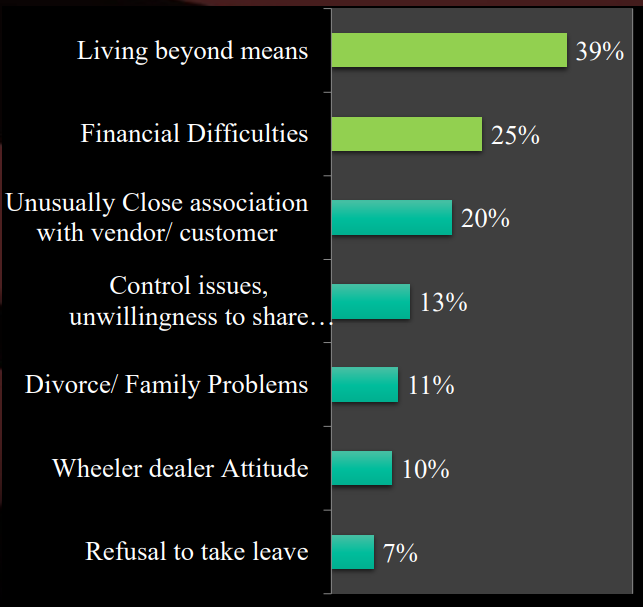
5. Types of Trigger
Red flags
- Living Beyond means (Lifestyle of employees)
- Financial difficulties
- Unusually close association with Vendor/Customer
- Control issues, unwillingness to share duties
- Divorce/family problems
- Wheeler-dealer attitude
- Refusal to take leave
- Behaviour of the person – Unfriendly and an introvert
Green flags
- Not asking for increment for a very long time
- Gift to employees
- First to enter the office last to leave
- Budget v/s Actual – at par/low
- No claims on reimbursement
- Payment done through Personal account/Credit card
- Sudden profit in an otherwise loss making business
- Excessive Supporting Documentations
- Excess Stock as compared to that recorded in books of accounts
6. Preventive Technique
Core Vigilance Committee – Proprietary
- Scanning of emails and hard disk
- Surprise intelligence check of employees
- Surprise vendor and customer visit
- Astound expense verification
Whistle Blow Technique
- Exposition of illicit activities being executed by fellow mate
- Communication via ethical helpline and email
- Independent committee to work on whistle blow
Test – Entry & Exit
- Entry Window – Eq test assuring intent, Background check
- Exit Window – Check on employee activities during notice period serving in the
organisation
7. Practical Case Studies
Disclaimer: Names in following examples have either been masked or renamed for confidentiality purposes
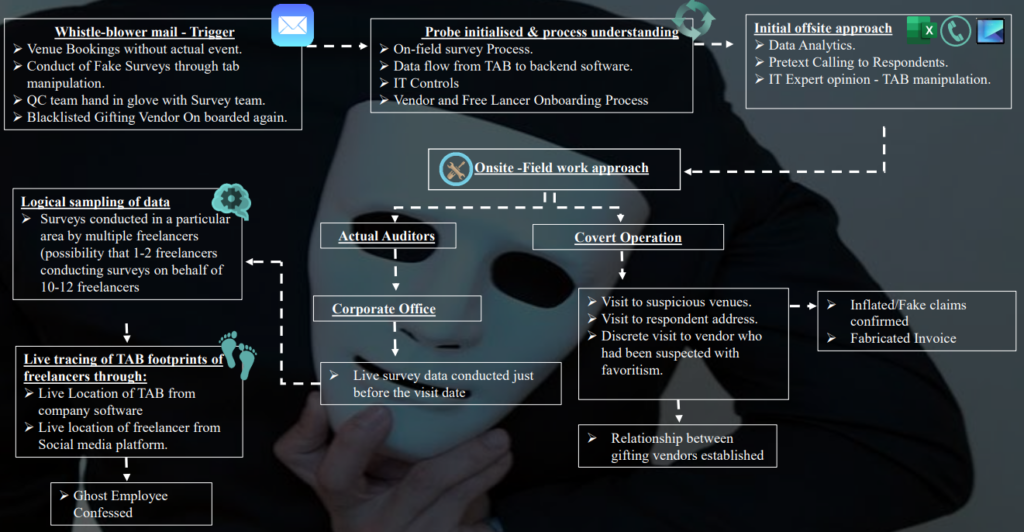
7.1 Project Mars – Research Company
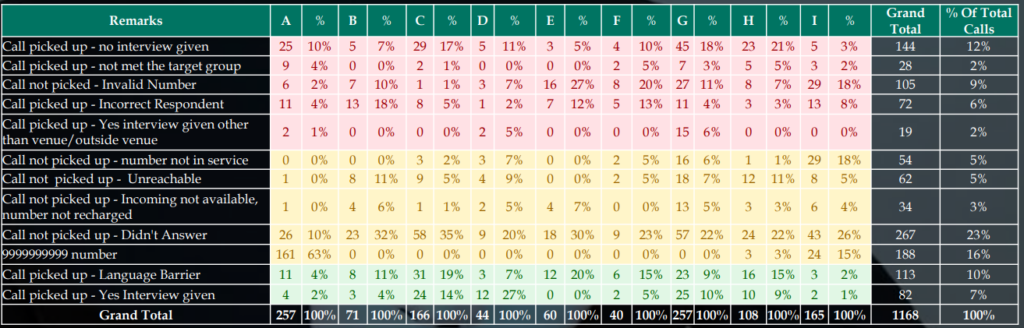
| Issue Cases | 32% |
| Neutral Cases | 52% |
| Positive Cases | 17% |
| Legends | |
| A | One employee – (400-600 minutes per day) |
| B | Personal Back Check – E.g.: Guntur Guntur |
| C | Telephonic Back Check – Tea Survey |
| D | Respondent Calling |
| E | Quality checker 1 (100% QC acceptance) |
| F | Quality checker 2 (100% QC acceptance) |
| G | Random Venue samples calling |
| H | Job1 – September 2022 |
| I | Discrete Calling – Smoking Survey |
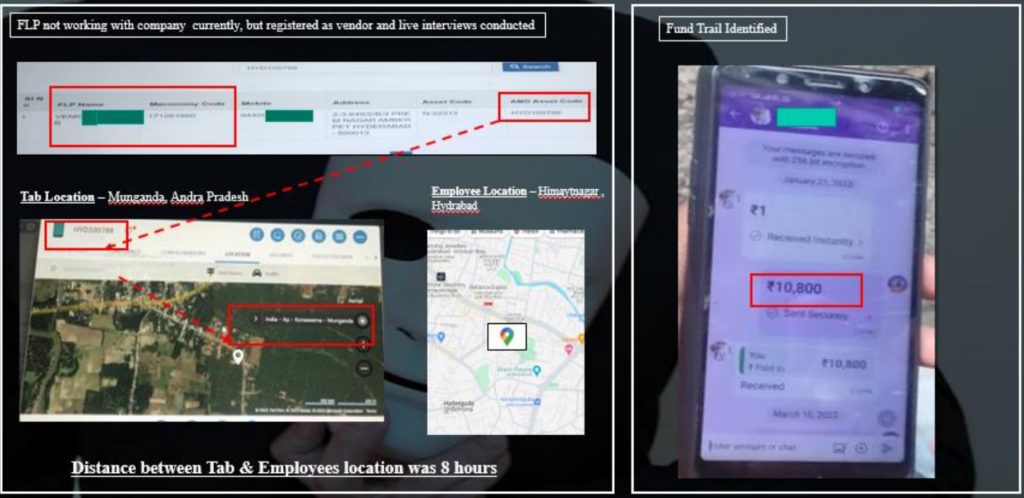
7.2 Document Fabrication
Disclaimer: Names in following examples have either been masked or renamed for confidentiality purposes
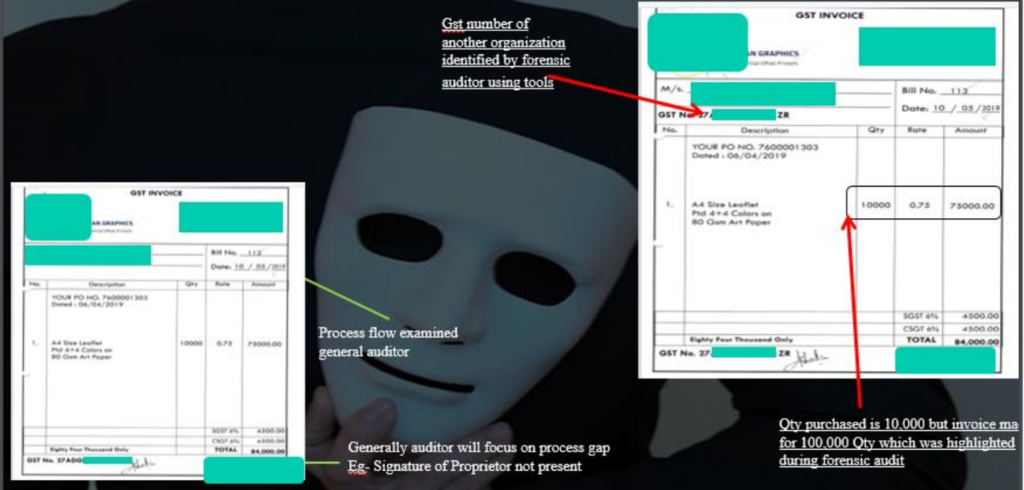
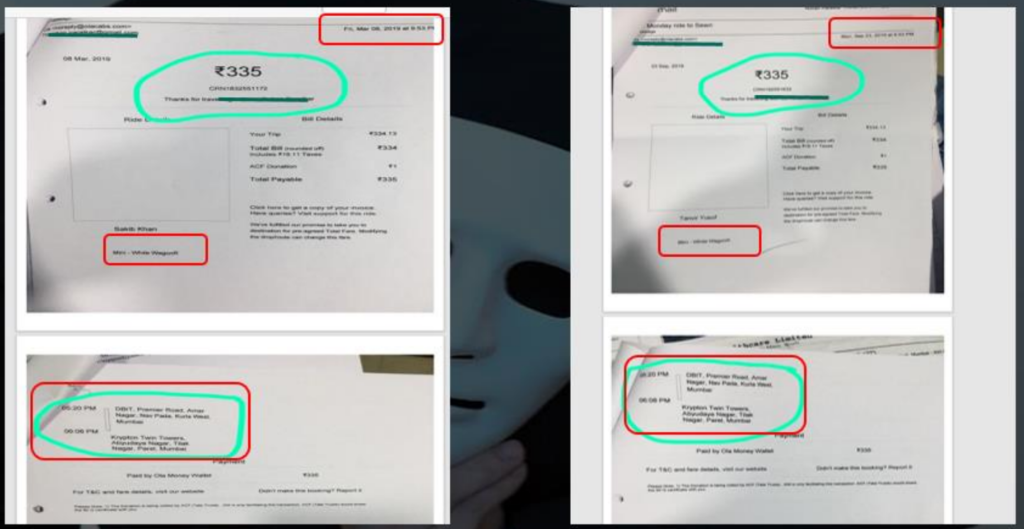
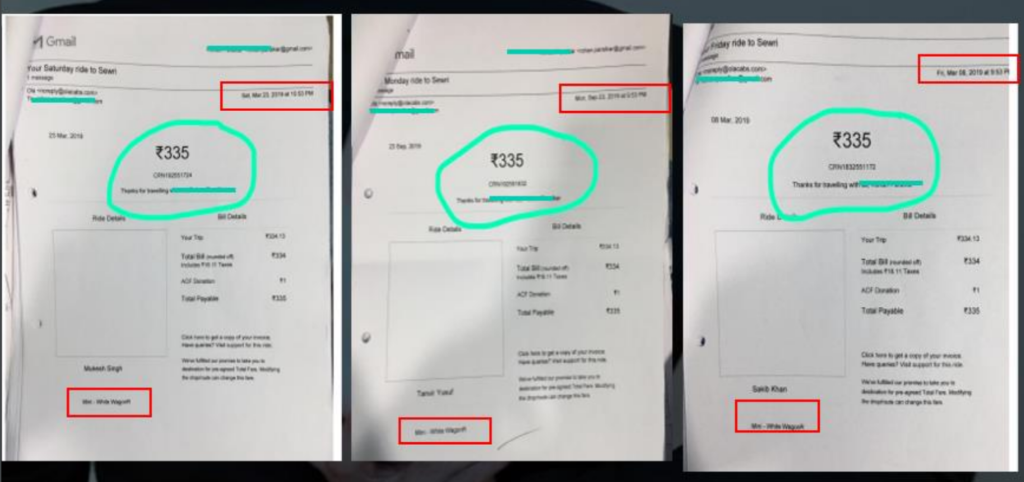

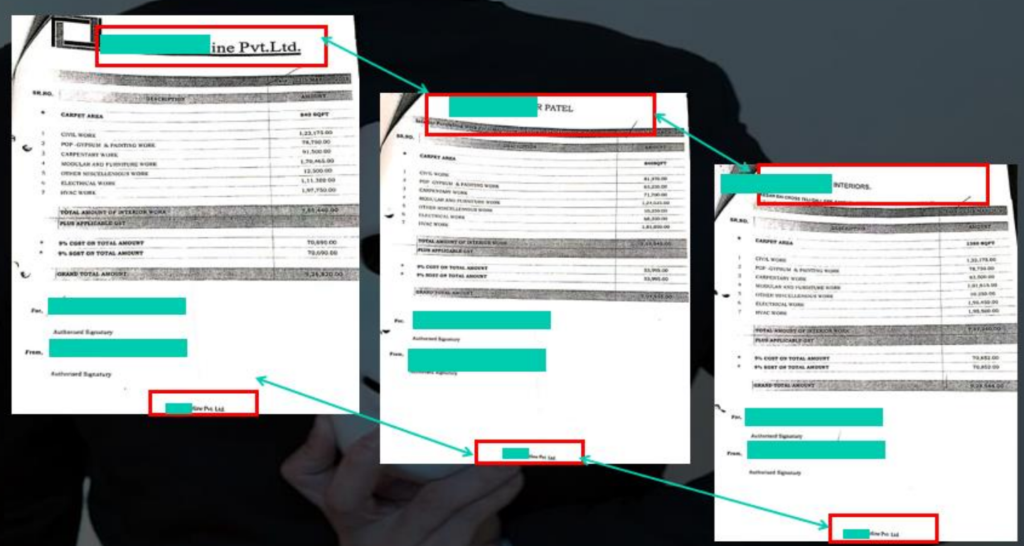
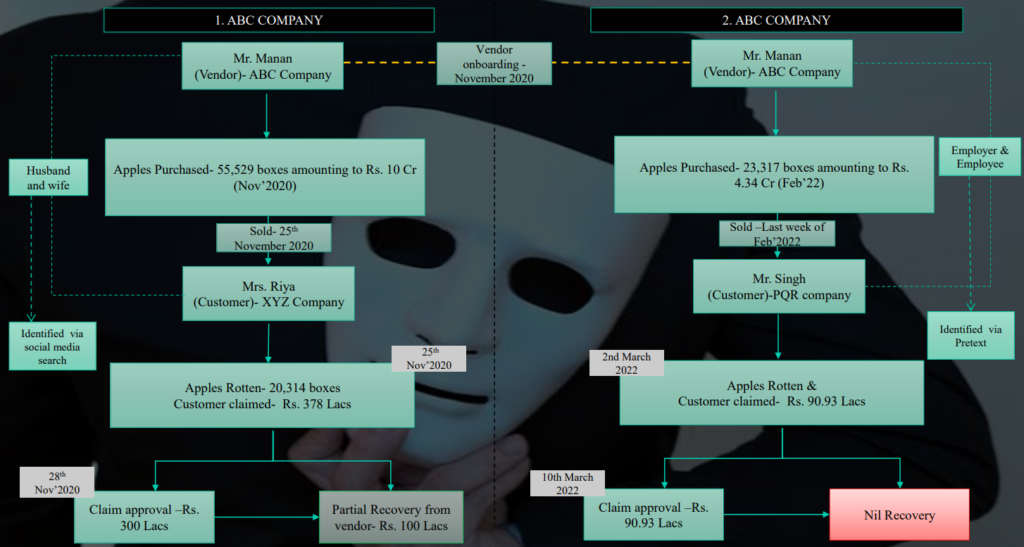
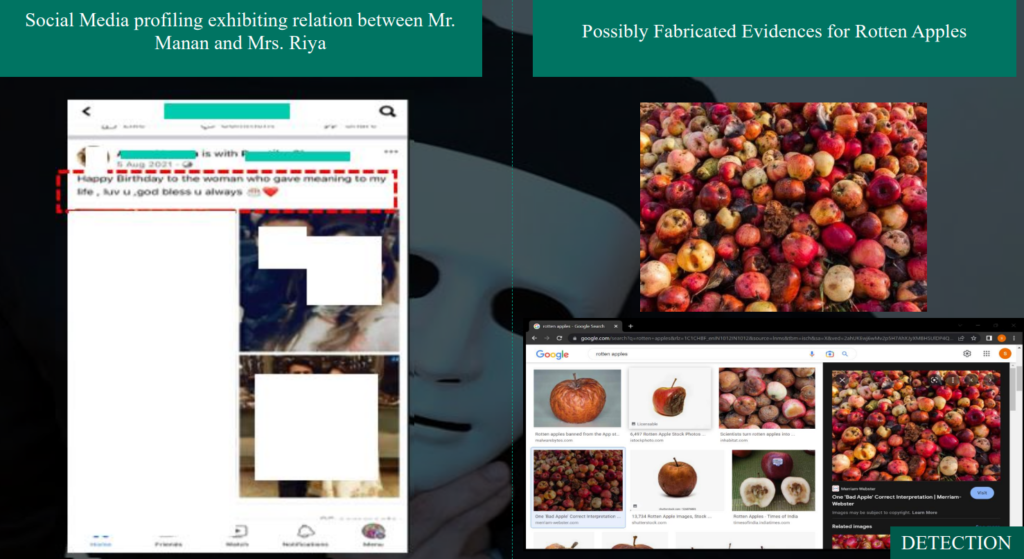
7.3 Rotten Fruit Case
Disclaimer: Names in following examples have either been masked or renamed for confidentiality purposes
1. Purchase and Sale – Related Party & Credit Note Raised
7.4 Vendor Reonboarding Case
Disclaimer: Names in following examples have either been masked or renamed for confidentiality purposes
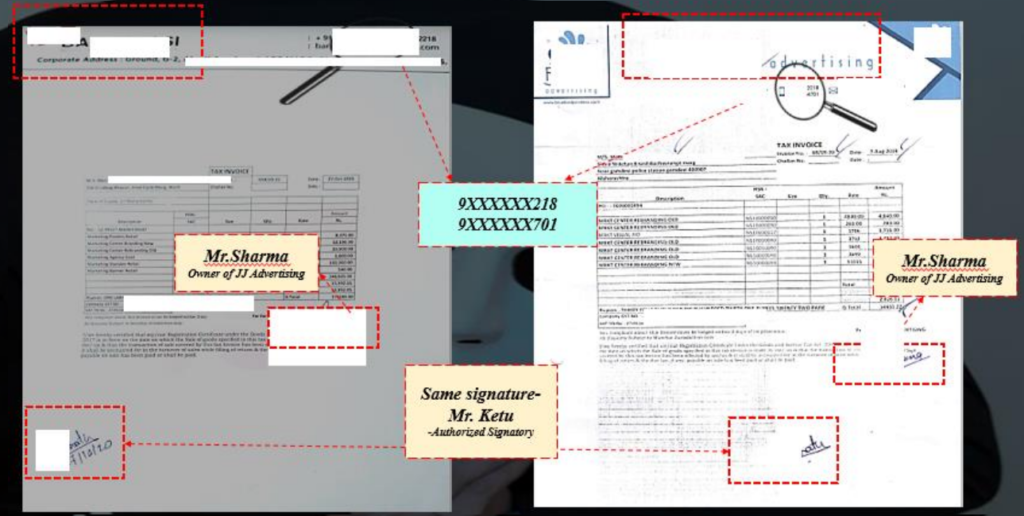
Blocked vendor opening another company and re-onboarded twice
- JJ Advertising was identified earlier as a suspected vendor due to multiple malpractices and was blacklisted
- Onboarding of new vendor – Bakshi Media with same owner
- Social Media Search for JJ Advertising shows Bakshi Media as a new brand of JJ Advertising
- Mr Sharma is identified as the owner of JJAdvertising & Bakshi Media
- On verification of the invoices, it was pertinent to note that contact numbers on both the invoices were same & authorized signatory for both the invoices is Mr Ketu
- The nature of services provided by both the vendors is similar
- Post blacklisting of Bakshi, same owner opened another company “XYZ Limited”
|
Vendor |
Total Business | |
| Feb’19-Jan’20 |
Jan’20 – Oct-22 |
|
| Bakshii Media | 48,716 | 61,16,651 |
Evidence proving relation and common links between JJ Advertising & Bakshi Media
Modus Operandi/Detection Method used
| Sr. No. | Case Name | Modus Operandi | Trigger | Detection Method used |
|
1 |
Project Brahmastra – Listed FMCG | Conflict of interest – Vendor opening shell company in wife’s and employee’s name and reversing transactions worth crores. Direct loss to company. | Multiple Credit notes raised giving reason of damaged products | Digital Forensic Social Media Profiling Pretext Calling |
|
2 |
Project Dabang – Listed Healthcare Company | Blacklisted vendor getting into the system by opening another company in own name and getting on boarded more than thrice. | Psychometric Test & SCAN | Digital Forensic |
|
3 |
Project Mars – Research Company | 1. Compromising on quality by providing report to clients with dummy data figures and quality supervisor manipulating sample of checking.
2. Inflated reimbursement bills of hotels. |
Whistle blower complaint |
1. Data Analytics Pretext Calling
2. Mystery Visit |
|
4 |
Project Houseful- Logistics & CHA | Accountant transferred amount payable (₹ 45 lakhs) to their own account thereby bypassing the authority matrix. Moreover, manipulated audit scoping keeping vouchers below ₹ 5 lakh out of scope. | Huge sum of outstanding amount to Vendor | Confirmation with vendor and re-assessing audit scope. |
|
5 |
Project Jalwa -Fashion Industry | Product Design Theft by ex-employee and sale of design duplicate under former company’s label. | Whistle blower complaint | Vigilanance & surveillance Pretext on Suspect |
|
6 |
Project Jupiter- Automobile Company | Teeming and Lading , Cash larceny | Customer following up on delivery status indicating payment completion however still outstanding as per books
. |
Confirmation with remaining customers to find out particulars regarding payment. |
|
7 |
Project Venus- Listed CHA | Resignation of 8+ employees post data theft | Resignation of multiple employees at same time & customer were being approached | Covert operation |
|
8 |
Project Procurement – Financial Services Company | Procurement Fraud , Collusion | Whistle blowers complaint | Physical site visits, Redundant supportings submitted. |
|
9 |
Project Galaxy – IT Company | Conflict of interest – Employee routing tenders to another company in which he has common directorship. | Huge loss suffered by company | Detailed investigation |
|
10 |
Project Venus- Listed Healthcare Company | Breach of non compete and business diversion – Doctors violating on compete clause and opening their own labs and diverting business. | Sudden drop in revenue | Pretext & Covert Operation |
|
11 |
Project Apollo – Listed NBFC | Digital lending fraud via keeping known vulnerabilities open into loan software and subsequent loan disbursements without adequate income proof. | High NPA cases | Loan Portfolio scanning |
| 12 | Project Navrang – Listed company | Sale of counterfeit products by suspects. Product resale | Preventive mechanism | Counterfeit audit Covert operations |
| 13 | Mumbai based Hospital | Sale of counterfeit experience letters by nurse | Sudden increase in Standard of Living | Social Media profiling |
| 14 | Listed Construction Company | Dummy vendor creation and subsequent fund siphoning. | Personal Bill found | Detailed Investigation |
| 15 | Listed Healthcare Company | No physical existence of numerous vendors
Vendors operating from house premise Vendors conducting business from unreasonable structure. |
Preventive Activity | No physical existence of numerous vendors |
8. Digital Forensic – Walkthrough
8.1 Workflow
Stage 1 – Disk Imaging
- It involves entire system imaging including system files.
- Data Imaging happens on the basis of Binary codes created in the system.
Stage 2 – Processing of Data
- System creates hash value for each data so as to maintain the originality & enables to submit in court of law. If any of the contents of original files are changed after processing of data, new hash value is created.
- Also recovers deleted files by user.
Stage 3 – Carving
- Carving allows to recover all formatted files which were once a part of the system even if the computer has been formatted multiple times.
Stage 4 – Indexing
- An Index is like a data base of text strings extracted from files or space on an evidence image
Stage 5 – Review
- Review is based on keyword search which are general as well as specific to the ongoing project
- Unique searches of min 250 key words having minimal multiplier of 4
- Manual review of the files populated by the tool
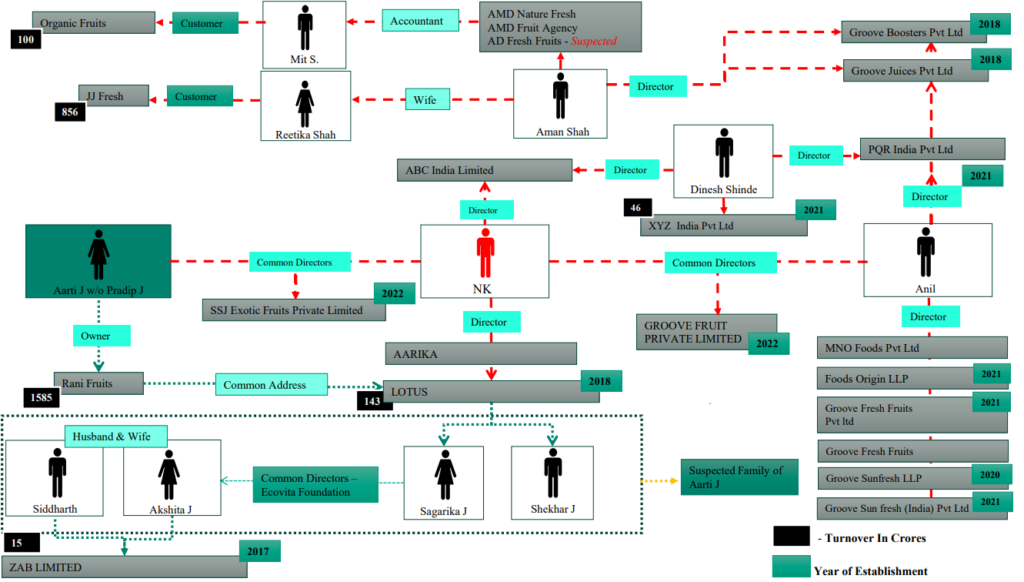
8.1 Report – Digital Forensic (Web Nexus)
Disclaimer: Names in following examples have either been masked or renamed for confidentiality purposes
9. Interrogation Techniques
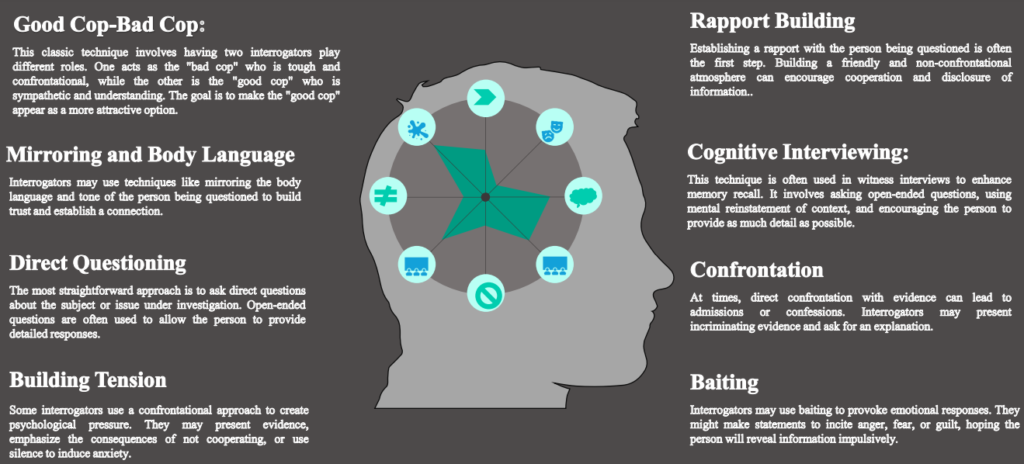
10. Care to Cure
10.1 Companies Act, 2013
Section 143(12) – Reporting by Auditors: If during the course of audit, the auditor has reason to believe that an offence of fraud involving an amount exceeding Rs. 1 crore or more is being or has been committed against the company by the officers or employees of the company, then the auditor shall report the matter to the Central Government.
If the amount involved in fraud is less than Rs. 1 crore, the auditor shall report the matter to the audit committee or Board within a period of 2 days from the date of his knowledge of fraud.
10.2 CARO 2020
CARO 2020 provides for specific requirements for reporting of fraud under clause 11.
- Has there been any fraud by the company or any fraud done on the company. If any such fraud has been noticed or reported any time of the year. If yes, nature and amount involved have to be reported.
- Whether the auditors of the company have filed a report in Form ADT-4 with the Central Government as prescribed under the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014.
10.3 Other Compliances
(Depends on industry and Company Composition)
- SEBI Reporting
- RBI Reporting
- Whistle-blow cases – mandatory status reporting by statutory auditor
- Regulatory bodies outside India, if requirement so persists
- Adherence to AML guidelines & ABAC guidelines
- EOW Reporting – ₹6 crore and above
11. Forensic – Prospects
11.1 Forecasting the Future – Emerging Trends in Forensic
Key insights
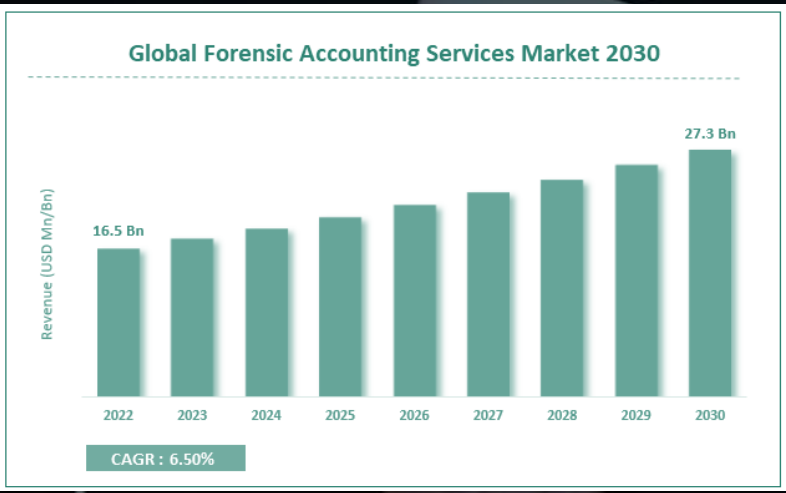
- The global Forensic Accounting Services market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 6.5% over the forecast period (2023-2030).
- In terms of revenue, the global Forensic Accounting Services market size was valued at around USD 16.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 27.3 billion, by 2030.
- The global Forensic Accounting Services market is being driven by the growing number of frauds in the BFSI sector.
12. Directories
12.1 Current trends Directory
- GDPR- Revolutionary Regulation
- SEBI tightens norms for Forensic Audit
- Introduction of Forensic Standards
- AI and Data mining in forensic
12.2 Theory Directory
- Men to men marking theory
- Cluster Theory
- Un-orthodox Theory
- Connect the dot theory
- Confirmation Bias Theory
- Time Bomb Theory
- Corporate Espionage
- Hydro Theory
- Orphan Fund Theory
12.3 Our Directory
- Maths on fraud
- 7 Eye’s on fraud detection
- CVC technique for fraud prevention
- In-house Tools like – Mail Scanning, SCAN, Mind Muneem
- Whistle–blow mechanism – Whistle-Eye
12.4 Take-Way
- Aura of forensic audit
- Practical Knowledge
- Point of View- General Auditor V/s Forensic Audit
- Forensic Readiness
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied




 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
